5 Ways Six Sigma Methodology Transforms Businesses

Six Sigma Methodology empowers businesses to achieve exceptional performance by refining processes and enhancing quality. Its structured approach ensures measurable results. For instance:
Achieving Six Sigma quality limits defects to 3.4 per million opportunities, ensuring 99.9997% accuracy.
Businesses adopting Six Sigma have reduced order processing time by 50% while maintaining 99.9% accuracy in automated systems.
Companies like General Electric and Motorola have reported billions in savings and significant improvements in product reliability. By leveraging this methodology and resources effectively, organizations can transform their systems and achieve sustainable success.
Key Takeaways
Six Sigma lowers mistakes to 3.4 per million chances, ensuring great quality.
The DMAIC method finds and removes waste, making processes work better.
Companies using Six Sigma have cut order times by half while staying accurate.
Six Sigma tools improve product quality by lowering mistakes and differences.
Knowing what customers want helps businesses meet and beat their needs.
Using data to make decisions helps find problems and track progress.
Six Sigma saves money, helping businesses make more profit.
Training workers builds a culture of improvement and gives teams more confidence.
Enhances Process Efficiency

Identifying and Eliminating Waste
The Role of the DMAIC Framework
The Six Sigma Methodology employs the DMAIC framework—Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control—to systematically identify and eliminate waste. This structured approach helps organizations pinpoint inefficiencies, such as redundant steps, bottlenecks, or unnecessary resource usage. By focusing on measurable data, teams can analyze processes to uncover root causes of waste and implement targeted improvements. For example, metrics like First Pass Yield (FPY) and Defects Per Unit (DPU) provide insights into process efficiency and quality. These measurements guide teams in reducing errors and optimizing workflows.
Metric | Description |
|---|---|
First Pass Yield (FPY) | Measures the percentage of units passing inspection on the first attempt, indicating process efficiency. |
Defects Per Unit (DPU) | Indicates the average number of defects per unit, helping identify areas for quality improvement. |
Cycle Time | Total time to complete a process, with reductions leading to increased efficiency and customer satisfaction. |
Examples of Waste Reduction Across Industries
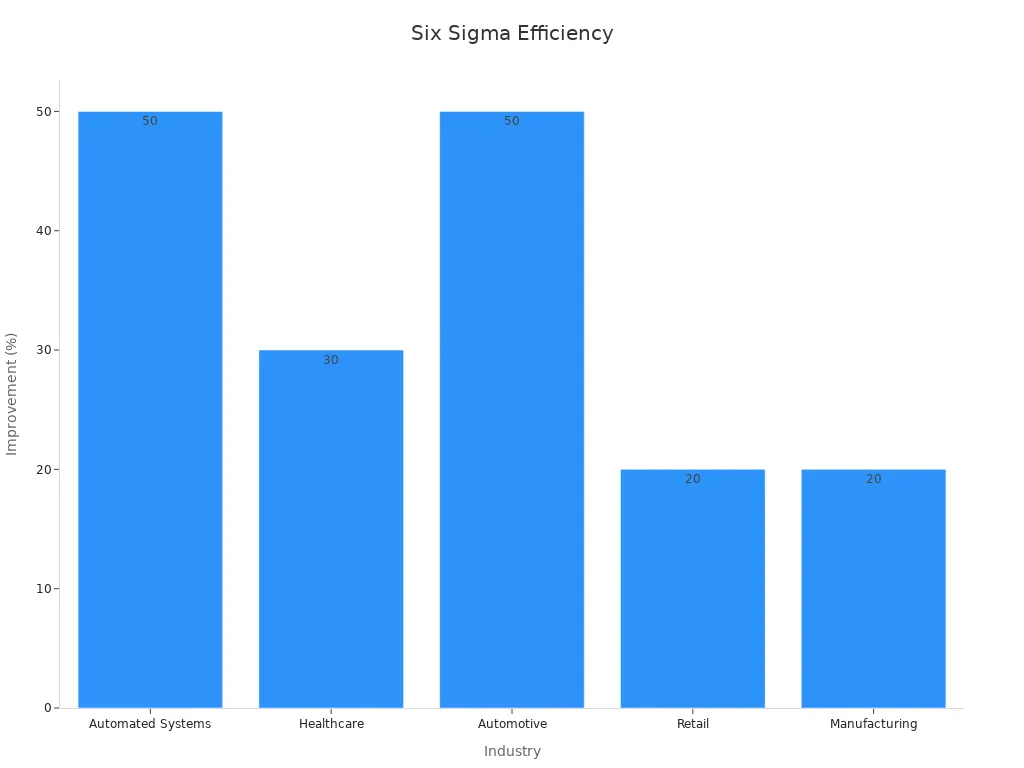
Organizations across various sectors have achieved remarkable results by applying Six Sigma Methodology to eliminate waste. In automated systems, companies reduced order processing time by 50% while maintaining 99.9% accuracy. Healthcare providers decreased average discharge times by 30%, improving patient throughput. The automotive industry cut defect rates by 50%, enhancing component quality. These examples demonstrate how Six Sigma transforms processes to deliver measurable improvements.
Industry | Improvement Description | Result |
|---|---|---|
Automated Systems | Reduced order processing time by 50% | 99.9% accuracy rates |
Healthcare | Reduced average discharge time by 30% | Improved patient throughput |
Automotive | Reduced defect rates by 50% in assembly line | Enhanced component quality |
Retail | Increased customer satisfaction scores by 20% | Addressed top complaint categories |
Manufacturing | Increased production efficiency by 20% and reduced costs | Streamlined operations |
Streamlining Workflows
Tools for Process Optimization
Six Sigma Methodology offers a variety of tools to streamline workflows. Value Stream Mapping (VSM) helps visualize processes and identify inefficiencies. Statistical Process Control (SPC) monitors performance to ensure consistency. Root Cause Analysis (RCA) uncovers underlying issues, enabling teams to address problems at their source. These tools empower organizations to optimize workflows, reduce delays, and enhance overall productivity.
Metric | Improvement Percentage |
|---|---|
Productivity | 20-30% |
Defect Reduction | Up to 40% |
Customer Satisfaction | Enhanced |
Case Study: Workflow Improvements in Healthcare
Healthcare systems have leveraged Six Sigma to streamline workflows and improve patient care. For instance, hospitals implemented process mapping to identify bottlenecks in patient discharge procedures. By addressing these inefficiencies, they reduced discharge times by 30%, leading to better patient throughput and satisfaction. This case highlights how Six Sigma tools can transform workflows in critical industries.
Improves Product and Service Quality
Reducing Defects and Variability
Statistical Analysis in Quality Control
Six Sigma Methodology emphasizes the use of statistical tools to enhance product and service quality. Statistical Process Control (SPC) is one such tool that monitors and controls processes to ensure consistent performance. By analyzing data trends, teams can identify variations that lead to defects. This proactive approach allows organizations to address issues before they escalate, ensuring higher quality standards.
Organizations using SPC have reported:
Defect reductions of up to 40%.
Faster response times to quality issues.
More consistent product performance.
Increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
These improvements demonstrate how statistical analysis can transform quality control processes, leading to better outcomes for both businesses and their customers.
Real-World Example: Automotive Industry
An automotive manufacturer applied Six Sigma to its assembly line to address variability in component quality. By implementing statistical tools and focusing on root cause analysis, the company achieved a 50% reduction in defect rates. This improvement not only enhanced the reliability of their vehicles but also strengthened customer trust in their brand. The success of this initiative highlights the tangible benefits of reducing variability through Six Sigma practices.
Meeting and Exceeding Customer Expectations
Voice of the Customer (VOC) in Six Sigma
Understanding customer needs is a cornerstone of Six Sigma Methodology. The Voice of the Customer (VOC) process gathers feedback to identify customer expectations and pain points. Teams use this information to align products and services with customer demands. By prioritizing VOC, organizations can deliver solutions that not only meet but exceed expectations.
For example, VOC data might reveal that customers value faster delivery times. Using Six Sigma tools, teams can streamline logistics processes to achieve this goal. This customer-centric approach fosters loyalty and enhances the overall customer experience.
Case Study: Enhancing Customer Satisfaction in Retail
A retail company utilized Six Sigma to address common customer complaints, such as long checkout times and limited product availability. By analyzing VOC data, the team identified key areas for improvement. They implemented process changes that reduced checkout times by 25% and improved inventory management. As a result, customer satisfaction scores increased by 20%. This case study illustrates how Six Sigma can drive meaningful improvements in customer experience.
Drives Data-Driven Decision Making
Leveraging Data for Business Insights
Importance of Metrics in Six Sigma
Metrics play a critical role in the Six Sigma Methodology. They provide measurable insights into process performance and help teams identify areas for improvement. Metrics such as Defects Per Million Opportunities (DPMO) and Process Capability Index (Cpk) allow organizations to evaluate the efficiency and quality of their operations. These measurements ensure that decisions are based on data rather than assumptions. By focusing on metrics, teams can track progress, set realistic goals, and achieve consistent results.
For example, DPMO helps quantify the number of defects in a process, while Cpk measures how well a process meets customer specifications. These metrics guide teams in making informed decisions that enhance both efficiency and quality. Organizations that prioritize data-driven metrics often experience improved operational performance and customer satisfaction.
Tools for Data Collection and Analysis
Six Sigma offers a range of tools to collect and analyze data effectively. Automated systems, such as Statistical Process Control (SPC) and Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), provide real-time insights into process performance. These tools enable teams to monitor trends, identify anomalies, and implement corrective actions promptly. Root Cause Analysis (RCA) further helps uncover the underlying causes of issues, ensuring that solutions address the root problem rather than just the symptoms.
For instance, SPC charts track process variations over time, allowing teams to maintain control and consistency. FMEA identifies potential failure points and assesses their impact, helping organizations mitigate risks before they occur. By leveraging these tools, businesses can make data-driven decisions that drive continuous improvement.
Predicting and Preventing Issues
Predictive Analytics in Six Sigma
Predictive analytics is a powerful component of the Six Sigma Methodology. It uses historical data and statistical models to forecast potential issues and optimize processes. Teams can identify critical quality characteristics and process variables that impact product performance. Automated data collection tools provide accurate, real-time measurements, enabling organizations to act proactively rather than reactively.
Key benefits of predictive analytics include:
Trend Analysis: Long-term data patterns reveal opportunities for process optimization.
Performance Metrics: Real-time quality indicators track improvement progress.
Risk Assessment: Predictive models identify potential quality risks before they impact production.
By integrating predictive analytics into their operations, organizations can reduce downtime, improve efficiency, and maintain high-quality standards.
Example: Preventing IT System Downtime
An IT services company implemented Six Sigma to address frequent system downtimes. By analyzing historical data, the team identified patterns that indicated potential failures. They used predictive models to forecast system performance and implemented preventive measures, such as upgrading hardware and optimizing software configurations. These actions reduced downtime by 40%, ensuring uninterrupted service for clients. This example highlights how Six Sigma's data-driven approach can prevent issues and enhance operational reliability.
Reduces Costs and Boosts Profitability
Lowering Operational Costs
Identifying Cost-Saving Opportunities
Organizations often face hidden inefficiencies that inflate operational costs. Six Sigma Methodology provides a structured approach to uncover and address these inefficiencies. By analyzing processes through tools like Value Stream Mapping and Root Cause Analysis, teams can identify areas where resources are wasted or underutilized. For example, companies have achieved significant savings by reducing errors in data entry, optimizing inventory management, and streamlining supply chains.
Several real-world examples highlight the cost-saving potential of Six Sigma. Kraft Foods implemented Lean Six Sigma in 2011, leading to a 4% improvement in Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). This improvement directly boosted profitability. Similarly, a technology company saved $2.3 million annually by reducing customer contact information errors from 15% to less than 1%. These initiatives demonstrate how Six Sigma helps organizations cut costs while maintaining or improving quality.
Case Study: Supply Chain Cost Reduction
A manufacturing company faced high operational costs due to inefficiencies in its supply chain. By applying Six Sigma tools, the team identified discrepancies in inventory management and delivery schedules. Enhanced data quality testing reduced inventory discrepancies from 12% to 0.5%, saving the company $4.2 million annually. Additionally, improved delivery accuracy increased customer satisfaction. This case study illustrates how Six Sigma transforms supply chain operations, leading to measurable cost reductions and improved efficiency.
Maximizing Return on Investment (ROI)
Measuring Financial Impact of Six Sigma Projects
Six Sigma projects often deliver substantial financial benefits by improving efficiency and reducing waste. Metrics such as Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ) and Return on Investment (ROI) help organizations quantify these benefits. For instance, General Electric reported nearly $700 million in corporate benefits within two years of adopting Six Sigma. This figure grew to over $2.5 billion within three years. Motorola also achieved remarkable results, saving over $16 billion by reducing product defect rates by more than 80%.
These examples highlight the financial impact of Six Sigma initiatives. By focusing on measurable outcomes, organizations can ensure that their investments in Six Sigma yield significant returns.
Example: ROI Improvements in Small Businesses
Small businesses can also benefit from Six Sigma's ROI-focused approach. For instance, a local manufacturing firm implemented Six Sigma to address high defect rates in its production line. By using tools like Statistical Process Control (SPC) and Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), the team reduced defects by 40%. This improvement not only lowered production costs but also enhanced customer satisfaction. The financial gains from these changes allowed the business to reinvest in growth initiatives, demonstrating how Six Sigma drives profitability even for smaller organizations.
Industry | |
|---|---|
Healthcare | Enhanced patient care with fewer errors and reduced costs. |
Financial Services | Improved customer service and cost savings through efficiency. |
Manufacturing | Reduced defects and increased efficiency leading to cost savings. |
Software Development | Reduced product defects and improved process management. |
By leveraging Six Sigma Methodology, businesses of all sizes can achieve measurable financial benefits, ensuring long-term success and sustainability.
Fosters a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Empowering Employees Through Training
Six Sigma Certification and Skill Development
Six Sigma Methodology emphasizes the importance of employee training and certification to build a skilled workforce. Certification programs equip employees with the tools and techniques needed to identify inefficiencies, reduce defects, and improve processes. These programs, such as Green Belt and Black Belt certifications, provide structured learning paths that enhance problem-solving skills and statistical analysis capabilities. Employees gain confidence in their ability to contribute to organizational goals, fostering a sense of ownership and accountability.
Organizations that invest in Six Sigma training often see measurable improvements in performance. For example, certified employees can use tools like Value Stream Mapping and Root Cause Analysis to streamline workflows and reduce waste. This not only boosts productivity but also creates a culture where employees feel empowered to drive change.
Encouraging Employee-Led Initiatives
A culture of continuous improvement thrives when employees take the lead in identifying and solving problems. Six Sigma encourages teams to propose and implement initiatives that align with organizational objectives. By involving employees in decision-making, companies tap into their unique insights and foster innovation.
Employee-led initiatives often result in significant improvements. For instance, a team in the automotive sector used Six Sigma tools to reduce defect rates by 50%, as shown in the table below. These successes demonstrate the value of empowering employees to take ownership of improvement projects.
Case Example | Improvement | Metric |
|---|---|---|
Healthcare | Reduced average discharge time | 30% |
Automotive | Reduced defect rates | 50% |
Retail | Increased customer satisfaction | 20% |
Sustaining Long-Term Success
Embedding Six Sigma into Organizational Culture
Sustained success requires embedding Six Sigma principles into the organization's culture. This involves integrating Six Sigma practices into daily operations, decision-making processes, and performance evaluations. Leaders play a crucial role by modeling Six Sigma behaviors and encouraging teams to adopt its methodologies.
Metrics such as Defects Per Million Opportunities (DPMO) and First Pass Yield (FPY) help organizations monitor long-term performance. These metrics ensure that improvements are not only achieved but also maintained over time. The table below highlights key metrics that demonstrate sustained success through Six Sigma.
Metric | Description |
|---|---|
Defects Per Million Opportunities (DPMO) | Measures the number of defects in a process per million opportunities for defects. A lower DPMO indicates a more efficient process. |
Sigma Level | Indicates the capability of a process to produce defect-free work. Higher Sigma levels signify better performance. |
First Pass Yield (FPY) | The percentage of units passing inspection on the first attempt, indicating process efficiency. |
Throughput Yield (TY) | Measures the percentage of units completing a process without defects, accounting for all process steps. |
Financial Impact | Assesses improvements in revenue, cost savings, and return on investment from Six Sigma projects. |
Quality Improvements | Evaluates enhancements in product and service quality, leading to increased customer satisfaction. |
Productivity Gains | Measures increases in output and efficiency, reducing lead times and waste. |
Employee Engagement | Reflects the involvement of employees in the improvement process, fostering a culture of continuous improvement. |
Sustainability | Ensures that improvements are long-lasting and embedded in the organization's culture and processes. |
Example: Continuous Improvement in Tech Companies
Tech companies have successfully embedded Six Sigma into their cultures to sustain long-term success. For example, a leading software firm used Six Sigma to improve its product development cycle. By analyzing process inefficiencies and implementing corrective actions, the company reduced defects and shortened lead times. These improvements enhanced customer satisfaction and increased market competitiveness.
This example illustrates how Six Sigma Methodology can drive continuous improvement in dynamic industries. Organizations that prioritize a Six Sigma culture not only achieve immediate gains but also build a foundation for sustained excellence.
Six Sigma Methodology has proven to be a game-changer for businesses across industries. By enhancing efficiency, improving quality, and fostering data-driven decisions, it delivers measurable results. Companies like General Electric and Motorola have reported billions in savings, with defect rates reduced by up to 80%. Honeywell achieved $1.2 billion in productivity improvements, showcasing the financial impact of this approach.
Company | Improvement Type | Financial Impact |
|---|---|---|
General Electric | Corporate benefits | Nearly $700 million in 1997, over $2.5 billion in 1999 |
Motorola | Product defect reduction | Over $16 billion in savings with 80% defect rate reduction |
Honeywell | On-time delivery & reliability | $1.2 billion from productivity improvements in 2012 |
The methodology also drives operational cost reductions of 15-25% and productivity improvements of 20-30%. These results highlight its ability to transform businesses while fostering a culture of continuous improvement. Organizations can tailor Six Sigma to their unique needs, ensuring long-term success and sustainability.
Benefit Type | Improvement Percentage |
|---|---|
Productivity Improvement | 20-30% |
Defect Reduction | Up to 40% |
Operational Cost Reduction | 15-25% |
Resource Utilization | 30-40% |
Waste Reduction | 20-30% |
Start exploring how Six Sigma can revolutionize your business today.
FAQ
What is Six Sigma, and why is it important for businesses?
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that improves processes by reducing defects and variability. It helps businesses achieve higher efficiency, better quality, and cost savings. Companies use Six Sigma to meet customer expectations and gain a competitive edge in their industries.
How does Six Sigma differ from Lean methodology?
Six Sigma focuses on reducing defects and variability using statistical tools. Lean methodology emphasizes eliminating waste and improving flow. While both aim to enhance efficiency, Six Sigma relies on data analysis, whereas Lean prioritizes process simplification. Many organizations combine both for maximum impact.
Who can benefit from Six Sigma training and certification?
Employees at all levels, from entry-level staff to senior management, can benefit from Six Sigma training. Certifications like Green Belt and Black Belt equip individuals with problem-solving skills and statistical tools, enabling them to lead improvement projects and contribute to organizational success.
How long does it take to see results from Six Sigma projects?
The timeline depends on the project's complexity and scope. Small-scale projects may show results within weeks, while larger initiatives could take months. Organizations often see measurable improvements in efficiency, quality, and cost savings within the first year of implementation.
Can small businesses implement Six Sigma effectively?
Yes, small businesses can implement Six Sigma successfully. The methodology is scalable and can be tailored to fit smaller operations. By focusing on key processes and using tools like Root Cause Analysis, small businesses can reduce costs, improve quality, and enhance customer satisfaction.
What industries commonly use Six Sigma?
Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, retail, finance, and technology frequently use Six Sigma. It helps manufacturers reduce defects, healthcare providers improve patient care, and retailers enhance customer satisfaction. The methodology's versatility makes it applicable across various sectors.
What are the key tools used in Six Sigma?
Six Sigma employs tools like Value Stream Mapping, Statistical Process Control (SPC), and Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA). These tools help teams analyze processes, monitor performance, and identify improvement opportunities. They ensure data-driven decisions and sustainable results.
How does Six Sigma support continuous improvement?
Six Sigma fosters a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging employees to identify inefficiencies and propose solutions. Training programs and certifications empower teams to use data-driven tools. Organizations embed Six Sigma principles into daily operations to sustain long-term success.



