A Beginner’s Guide to Automating Business Processes

Many employees spend hours each week on repetitive data entry or managing Hiring Systems. These manual tasks often lead to mistakes, delays, and frustration. Businesses face challenges like human error, inefficiency, and limited scalability.
Challenge Type | Description |
|---|---|
Human Error | Manual workflows are susceptible to mistakes like data entry errors, leading to financial losses. |
Inefficiency | Time-consuming repetitive tasks delay projects and hinder productivity. |
Lack of Visibility | Difficulty in tracking task progress and identifying bottlenecks. |
Limited Scalability | Challenges in scaling processes as the business grows, affecting workload management. |
Dependency on Individuals | Workflow disruptions occur if key personnel are unavailable. |
Inefficient Collaboration | Miscommunication and delays arise from manual task delegation and inter-department communication. |
Compliance Risks | Lack of standardized processes increases the risk of regulatory non-compliance. |
Difficulties in Data Analysis | Manual data management is slow and error-prone, complicating accurate reporting. |
Automation offers a solution. By choosing to Automate Business Processes, companies gain efficiency and reduce errors. Recent data shows that 30% of IT professionals report time savings when automation tools support Business Management. Anyone can start with basic Knowledge and simple tools to make work easier.
Key Takeaways
Automating business processes reduces repetitive tasks, saving time and increasing productivity by 25-30%.
Automation minimizes human errors, leading to a 40-75% reduction in mistakes and protecting your business's reputation.
Choosing the right processes to automate, like data entry and scheduling, can significantly enhance efficiency.
Using tools like Power Automate and Zapier allows businesses to automate tasks without needing coding skills.
Setting clear goals for automation helps measure success and aligns with broader business objectives.
Regular monitoring and maintenance of automated processes ensure consistent performance and quality.
Involving employees in the automation process fosters acceptance and helps identify areas for improvement.
Small businesses can benefit from automation just as much as large companies, enhancing competitiveness and growth.
What Is Business Process Automation?
Business process automation (BPA) uses technology to complete business tasks with little human help. Industry experts describe BPA as a way to use advanced tools to handle activities that help organizations reach their goals. These activities can include producing products, onboarding new employees, or managing customer requests. BPA often connects different departments and automates steps in a workflow, which improves both speed and accuracy.
Core Concepts
Several core ideas form the foundation of BPA:
BPA uses software applications to automate and manage workflows.
Integration tools connect BPA systems with other business software, allowing smooth data flow.
A user-friendly interface lets employees monitor and manage automated processes.
Analytics and reporting tools give insights into how processes perform.
Security features protect sensitive data and help meet regulations.
A typical automated process includes:
Triggers that start the process
Inputs such as data or materials
Steps that outline the actions needed
Decision points where the system chooses the next step
Handoffs between teams or systems
Outputs, which are the final results
Downstream effects, where outputs support other processes
Key Benefits
Automating business processes brings many measurable benefits. Organizations that Automate Business Processes often see improvements in efficiency, cost savings, and employee satisfaction.
Efficiency Gains
Automated processes reduce manual work and speed up operations. According to recent studies, productivity increases by 25-30% on average when companies Automate Business Processes. Employees spend less time on repetitive tasks and more time on valuable work.
Cost Reduction
Businesses also report significant cost savings. Many organizations achieve a return on investment within 12 months. Labor costs drop, and error rates decrease, which saves money on corrections and lost opportunities.
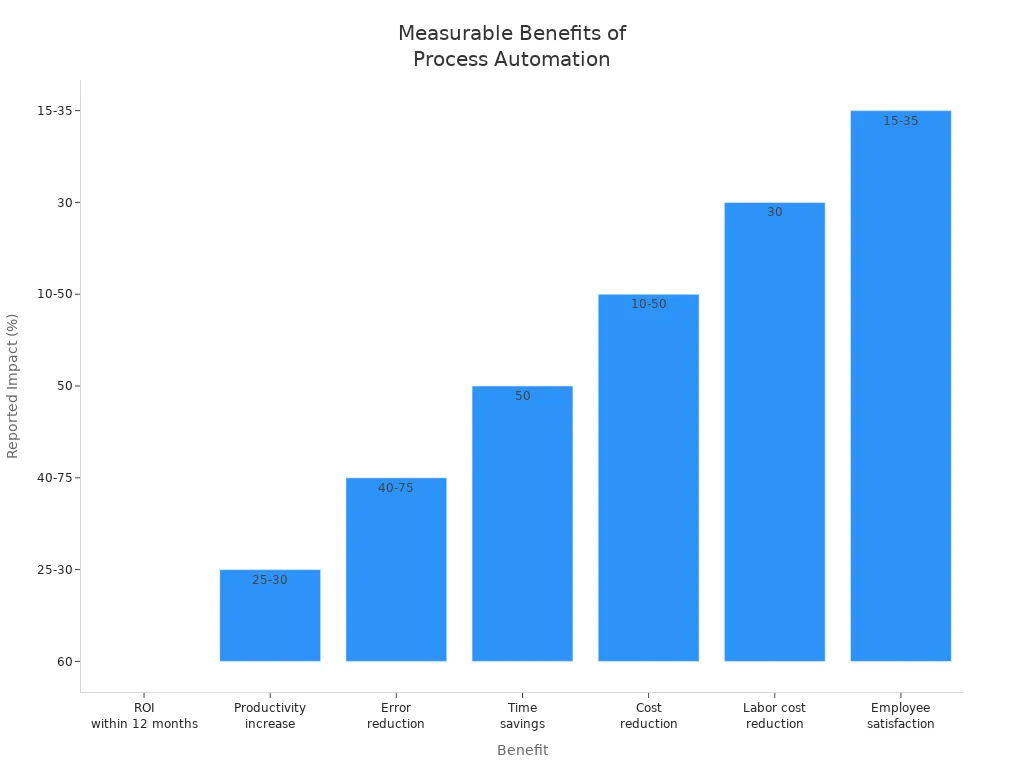
Benefit | Statistic/Impact |
|---|---|
ROI within 12 months | 60% of organizations achieve ROI |
Productivity increase | 25-30% average increase |
Error reduction | 40-75% fewer errors |
Time savings | 50% of time saved (73% of IT leaders) |
Cost reduction | 10-50% lower costs |
Labor cost reduction | 30% report reduced labor costs |
Employee satisfaction | 15-35% improvement |
Customer service improvement | Enhanced service delivery |
Visibility and transparency | Improved accountability and insights |
Common Myths
Many small businesses believe some common myths about automation:
Automation replaces human interaction and makes businesses impersonal. In reality, it frees employees to focus on personal outreach.
Some think automation removes the human touch from client communications. Instead, it ensures prompt responses and better service.
If a process needs some manual steps, people assume it cannot be automated. However, automation can still help with other parts of the process.
Automation is not just for marketing; it can improve any repetitive task.
Many believe only large companies can benefit, but small businesses also gain efficiency and manage orders better.
Some worry automation will make employees feel like machines, but it actually reduces stress and workload.
Automation does not lead to layoffs; it can help secure jobs by lowering overhead costs.
Note: Understanding these facts helps businesses make informed decisions about automation.
Why Automate Business Processes?
Business leaders often look for ways to improve how their companies work. Automating business processes offers several strategic advantages. Companies that choose automation can operate more efficiently, reduce mistakes, and help employees focus on meaningful work. These benefits support business growth and long-term success.
Streamlining Operations
Automation helps organizations run smoother by connecting different systems and reducing manual steps. Many businesses now use automation to handle daily tasks. The following table shows how companies use automation and the results they see:
Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
Adoption Rate | Over 71% of businesses have adopted some form of automation. |
AI Utilization | 45% of businesses utilize AI-driven tools to enhance workflows. |
Efficiency Gains | Targeted process automation delivers productivity gains of 20-40%. |
Cost Reduction | Companies can expect a 10-20% reduction in labor costs in one year. |
AI and automation eliminate repetitive tasks, which reduces human error and allows teams to focus on important projects. For example, AI-powered chatbots can manage thousands of customer questions at once, improving satisfaction rates. In human resources, AI tools simplify hiring and onboarding, making the process faster and more engaging for new employees.
Reducing Errors
Manual work often leads to mistakes. Automation helps companies avoid these errors by standardizing processes and checking data in real time. The following list highlights how automation reduces errors:
Automation of data entry minimizes manual typing errors.
Real-time data validation catches mistakes before data is saved.
Standardized processes reduce variability and human mistakes.
Companies that use automation report a 50-70% reduction in errors. Automated systems also send alerts to prevent missed deadlines and overlooked steps. By reducing errors, businesses save money and protect their reputation.
Freeing Up Employees
When companies Automate Business Processes, employees spend less time on repetitive tasks. This shift allows workers to focus on creative and valuable activities. Job satisfaction increases when people use their skills for meaningful work. Studies show that 32% of workers have left a job because of poor technology, and 49% of frustrated employees consider leaving. Automation improves job satisfaction, which leads to higher motivation and lower turnover rates.
Tip: Happy employees are more productive and help drive innovation in the workplace.
Automation supports business growth by making operations more efficient, reducing costly mistakes, and helping employees do their best work. As more organizations adopt automation, they gain a competitive edge and prepare for future challenges.
Identify Processes to Automate
Choosing the right processes to automate can help a business save time and reduce mistakes. Not every task fits automation, so teams need to look for the best candidates. By following a clear approach, companies can focus on areas that bring the most value.
Repetitive Tasks
Tasks that repeat often and follow the same steps make strong candidates for automation. Small businesses usually start with activities that take up a lot of time and do not require much decision-making. Common examples include:
Appointment scheduling
Calendar management
Social media marketing
Virtual mail services
Virtual reception services
Inventory management
Customer relationship management
Marketing
Employee management
Reporting
Email marketing campaigns
These tasks often slow down teams and lead to errors when done by hand. Automating them allows employees to focus on more important work.
Process Mapping
Before a business can Automate Business Processes, it needs to understand how each process works. Process mapping helps teams see every step and spot areas for improvement. Best practices for mapping include:
Involve key stakeholders early to clarify workflows and build support.
Use real-world data to make sure the map matches actual work.
Update process maps regularly to keep them accurate.
Limit the scope to one process at a time for clarity.
Standardize symbols and terms so everyone understands the map.
Add feedback loops for ongoing improvement.
Focus on activities that add value.
Identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
Look for steps that can be automated.
Clearly mark decision points to show process complexity.
A clear process map helps teams find steps that slow down work or cause errors. It also makes it easier to explain changes to everyone involved.
Tip: Use simple flowcharts or diagrams to visualize each step. This makes it easier to spot where automation can help.
Prioritizing for Impact
Not all processes offer the same benefits when automated. Teams should use specific criteria to decide which tasks to tackle first. The table below shows important factors to consider:
Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
Frequency and volume | How often the task is performed |
Error rates | The number of mistakes made in the process |
Time sensitivity | The urgency of completing the task |
Standardization | The extent to which the task follows set rules |
To maximize impact, businesses should:
Analyze current processes to find bottlenecks and redundancies.
Set clear, measurable goals for automation.
Choose a platform that works well with existing systems.
Start with pilot projects for high-impact tasks.
Test and validate automated workflows.
Manage change to help teams adjust.
Monitor and optimize for ongoing improvement.
By starting with high-volume, low-complexity tasks, companies can see quick wins and build confidence in automation.
Tools to Automate Business Processes
Many businesses use automation tools to save time and reduce errors. These tools help teams work faster and more accurately. Companies can choose from many platforms, each with unique features and strengths.
Popular Platforms
Several leading platforms help businesses Automate Business Processes. These tools support a wide range of tasks, from simple reminders to complex workflows.
Power Automate
Power Automate, developed by Microsoft, allows users to create automated workflows between apps and services. It connects with popular tools like Outlook, SharePoint, and Teams. Users can set up triggers, such as receiving an email, to start a series of actions. Power Automate offers templates for common business tasks, making it easy for beginners to get started.
Zapier
Zapier is a cloud-based platform that links over 3,000 apps. It helps users build "Zaps," which are automated workflows that move information between apps. For example, Zapier can add new email subscribers to a spreadsheet or send notifications to a chat app. The platform does not require coding, so anyone can use it to automate daily tasks.
IFTTT
IFTTT stands for "If This Then That." This tool lets users create simple automation rules, called "applets." IFTTT connects apps and devices, such as calendars, smart lights, and social media accounts. Users can set up actions like posting a tweet when a new blog goes live or turning on lights at a certain time. IFTTT is popular for both business and personal use.
Note: Other key players in business process automation include Laserfiche, TIBCO Software, OptimumHQ, Kissflow Inc., Oracle, Zoho Corporation, IBM, and Appian. North America is expected to hold the largest market share, with cloud-based solutions leading the way.
Choosing the Right Tool
Selecting the best automation tool depends on a company’s needs and goals. Teams should compare features, ease of use, and how well the tool fits with existing systems.
Factor | Description |
|---|---|
Look for tools that offer advanced features like AI-powered lead qualification and automated responses. | |
Scalability and flexibility | Choose a tool that can grow with your business, offering customizable workflows and adaptable pricing. |
Integration and compatibility | Ensure the tool integrates seamlessly with your existing marketing and sales stack. |
Pricing and ROI | Calculate the total cost of ownership and evaluate the potential return on investment. |
Other important considerations include:
Software features that eliminate repetitive tasks
Customization options for unique workflows
Visibility into project status to spot bottlenecks
User-friendliness for easy adoption
Strong security for sensitive information
Analytics and reporting to track performance
Tip: Start with a free trial or demo to see if the tool meets your needs before making a commitment.
Choosing the right platform helps businesses Automate Business Processes efficiently and supports long-term growth.
Set Up Your First Automation

Setting up your first automation can feel overwhelming, but a clear plan makes the process manageable. Many organizations, including clients at systems and teams, have followed these steps to successfully launch their first automated workflow. They often report faster task completion, fewer errors, and improved team satisfaction. This section provides a practical guide to help beginners achieve similar results.
Preparation Steps
Before building an automated workflow, teams need to prepare. Preparation ensures that the automation aligns with business goals and runs smoothly.
Define Your Goal
Start by setting a clear goal. Teams should ask, "What do we want to achieve with automation?" Goals might include reducing manual data entry, speeding up approvals, or improving customer response times. Defining a goal helps measure success later.
Tip: Choose a goal that supports larger business objectives and addresses a real pain point.
Gather Information
Next, gather all necessary information about the process. Teams should map out each step, identify who is involved, and collect any data or documents needed. This step often includes:
Listing each task in the process
Identifying repetitive or rules-based steps
Noting current challenges or bottlenecks
A detailed process map helps teams spot inefficiencies and decide which steps to automate first.
Preparation Checklist:
Set a tangible goal tied to business objectives.
Select a process that is repetitive and rules-based.
Map out the process in detail.
Evaluate automation tools for compatibility and ease of use.
Plan a small pilot project.
Communicate with employees and provide training.
Prepare to monitor and improve the workflow.
Build a Simple Workflow
With preparation complete, teams can begin building their first automated workflow. Most automation platforms use a visual interface, making it easy to design and adjust workflows.
Select Triggers
A trigger starts the automation. Teams should choose an event that signals the process to begin. Common triggers include:
Receiving a new email
Submitting a form
Adding a new row to a spreadsheet
Scheduling a calendar event
Selecting the right trigger ensures the workflow starts at the correct time.
Add Actions
After setting the trigger, add actions that the automation will perform. Actions might include:
Sending an email notification
Updating a database
Creating a task in a project management tool
Generating a report
Teams should arrange actions in the order they need to happen. Many platforms allow users to drag and drop actions, making the process straightforward.
Note: Start with a simple workflow to build confidence. Automate one or two steps before adding complexity.
Test and Troubleshoot
Testing ensures the automation works as intended. Teams should follow a structured approach to catch issues early.
Testing Steps:
Simulate real-world conditions to see how the automation performs.
Involve stakeholders in user acceptance testing to confirm usability.
Check performance under different loads.
Review security settings to protect sensitive data.
Common challenges for beginners include technical difficulties, integration issues, and user resistance. Teams can overcome these by starting small, choosing user-friendly tools, and providing training. Clients at systems and teams often find that involving employees early and offering support leads to smoother adoption and better results.
Callout: If the workflow does not work as expected, review each step, check for errors, and consult the tool’s support resources. Many platforms offer helpful guides and active user communities.
By following these steps, teams can Automate Business Processes with confidence. A successful first automation builds momentum and encourages further improvements across the organization.
Automation Best Practices
Monitor and Maintain
Successful automation does not end after launching a workflow. Teams must monitor and maintain automated processes to ensure they deliver consistent results. Real-time monitoring tools help detect issues as soon as they appear. Business Activity Monitoring (BAM) provides instant insights into process performance. Regular audits keep data quality high and reveal areas for improvement. Teams should also collect user feedback and foster a culture of continuous improvement. Change management strategies help users adapt to new systems and keep workflows running smoothly.
Use robust data collection and regular audits to maintain quality.
Apply real-time monitoring for immediate issue detection.
Encourage feedback from users to identify pain points.
Support change management to help teams adjust.
Promote ongoing improvement for long-term success.
Tip: Monitoring automated workflows helps prevent small problems from becoming major disruptions.
Data Security
Protecting data is a top priority when businesses Automate Business Processes. Automation can introduce risks such as compliance issues, security gaps, and ripple effects across departments. Organizations must address these risks to maintain customer trust and meet regulations. Strong access controls, real-time monitoring, and regular risk assessments help safeguard sensitive information. Training employees on security best practices also reduces the chance of insider threats.
Risk Type | Description | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
Compliance Risks | Automated processes can lead to compliance issues if not properly managed. | Conduct risk assessments and ensure compliance checks. |
Data Security Gaps | Security gaps can expose sensitive data to cyber threats. | Install strong access controls and use real-time monitoring. |
Ripple Risks | Failures in one automated process can affect others, creating widespread issues. | Regularly assess interconnected risks across departments. |
Process Failures | Errors in automation can lead to productivity losses. | Monitor processes continuously and correct issues promptly. |
Conduct risk assessments before and after automation.
Install access controls with role-based permissions.
Use monitoring tools to detect unusual activity.
Check compliance with industry standards regularly.
Train teams to recognize and respond to threats.
Note: Balancing security with usability ensures that automation supports business goals without exposing the organization to unnecessary risks.
Optimize Workflows
Optimizing automated workflows leads to better performance and greater value. Teams should start by mapping existing processes to spot inefficiencies. Focusing on high-impact workflows first allows for quick wins and easier scaling. User-friendly solutions encourage adoption and reduce errors. Involving stakeholders early ensures that workflows meet real business needs. Continuous monitoring and regular adjustments keep processes efficient over time.
Map current workflows to identify automation opportunities.
Begin with high-impact tasks but plan for future growth.
Choose solutions that are easy for everyone to use.
Gather input from key stakeholders.
Monitor performance and adjust as needed.
Other techniques include process mapping, standardization, and cross-functional collaboration. Lean principles, Six Sigma, and Agile methods also help teams maximize value and minimize waste.
Callout: Regularly reviewing and refining automated workflows ensures that businesses stay agile and competitive.
Overcome Common Challenges
Automating business processes brings many benefits, but teams often face obstacles during implementation. Understanding these challenges helps organizations prepare and respond effectively.
Technical Hurdles
Technical issues can slow down or even stop automation projects. Teams often encounter several common problems:
Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
Automation struggles with inefficient workflows, causing rapid failures in automated systems. | |
Lack of Process Standardization | Without clear rules, automation may create errors as teams use different methods for data entry. |
Integration with Legacy Systems | Older systems often lack the connections needed for automation. RPA tools can help bridge gaps. |
Managing Large Volumes of Data | Automation creates large data sets that can overwhelm traditional storage solutions. |
Ensuring Data Quality | Poor data quality leads to flawed results, so data validation and cleansing are essential. |
IT Security Concerns | Automation platforms handle sensitive data, making security best practices critical. |
Teams can overcome these hurdles by standardizing processes, validating data before automation, and using specialized tools to connect old and new systems. Regular security checks and strong access controls protect sensitive information.
Team Adoption
Getting everyone on board with automation tools can be difficult. People may resist change or feel unsure about new technology.
Absorb Adoption Burden: Create migration tools to help users transition smoothly. Phased rollouts to suitable teams keep the process focused and manageable. AWS Aurora saw wide adoption after offering migration support.
Successful organizations use several strategies to boost adoption:
Explain the “why” first. Teams need to understand the purpose behind automation.
Appoint internal champions. Influential team members can encourage others to embrace new tools.
Invest in proper training. Early onboarding improves long-term adoption rates.
Start with incremental rollouts. Phased launches achieve higher user adoption than company-wide changes.
Create custom guidelines and feedback loops. Internal rules and regular input help software fit unique workflows.
These steps help teams feel confident and supported as they learn new systems.
Continuous Improvement
Automation works best when teams commit to ongoing improvement. Businesses can foster a culture of learning and adaptation by:
Recognizing individuals who contribute to process improvements.
Using gamification, such as leaderboards, to reward positive changes.
Encouraging collaboration and sharing of best practices.
Aligning leadership and frontline employees for shared commitment.
Promoting trust and open communication in a blame-free environment.
Providing training and resources to empower employees.
Celebrating successes and viewing failures as learning opportunities.
Regularly reviewing and adjusting strategies to sustain progress.
Tip: Continuous assessment and adaptation keep automated processes effective and help organizations stay competitive.
By addressing technical, human, and process challenges, businesses can unlock the full potential of automation and build a foundation for lasting success.
Next Steps and Resources
Business process automation continues to evolve. Beginners can find many resources and communities to support their journey. The following sections highlight valuable learning materials, supportive communities, and practical steps for setting future goals.
Learning Materials
Many beginners want to build a strong foundation in business process automation. Several trusted resources offer clear explanations and step-by-step guides. These materials help users understand both the basics and more advanced topics.
What is Business Process Automation? A Comprehensive Guide: This guide explains the fundamentals of BPA and its benefits for organizations. It serves as a starting point for those new to automation. Read the guide
Automate a business process using Power Automate: This structured learning path introduces users to Power Automate. It teaches how to build workflows and prepares learners for certification. Explore the learning path
Tip: Start with a comprehensive guide to understand the big picture, then follow a structured path to build practical skills.
Community Support
Online communities give automation practitioners a place to share ideas, ask questions, and find solutions. These groups welcome both beginners and experienced users. The table below lists several active communities and their features.
Community Name | Description | Features |
|---|---|---|
Apeople | A global network for RPA and intelligent automation practitioners. | Message Board, Leaderboard, Groups, Events, Resources |
qBotica | Supports learning through mentoring and internships. | Mentoring, Internships, Partnerships |
RPA Live (Facebook Group) | The largest group for Robotic Process Automation discussions. | 10,000+ members, Medium activity |
Marketing Automation Experts (LinkedIn Group) | Focused on marketing professionals using automation tools. | 18,000+ members, Medium activity |
r/AutomatedMarketing (Reddit) | A niche group for marketing automation topics. | 1,600+ members, Low activity |
r/Automate (Reddit) | Covers a wide range of automation subjects. | 35,000+ members, Low activity |
Automators | Offers technical discussions and advice. | 2,700+ members, Medium activity |
Note: Joining a community helps users stay updated on trends, solve problems faster, and connect with peers.
Setting Future Goals
Setting clear goals guides the automation journey and measures progress. Many employees report that automation helps them finish tasks faster and increases job satisfaction. Engaging stakeholders early ensures that goals match business needs.
A step-by-step approach helps organizations expand automation successfully:
Align project and company goals. Automation should support the organization’s mission and strategy.
Determine project objectives. Use the SMART framework to set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound goals.
Record the status quo. Establish baseline key performance indicators (KPIs) before starting automation.
Quantify results. Compare KPIs after implementation to measure improvements.
Continuous monitoring and adjustment. Review KPIs regularly to keep automation aligned with business goals.
Businesses should also plan for scalability. Flexible goals help organizations adapt to growth and changing market needs.
Callout: Regular goal-setting and review keep automation efforts on track and ensure lasting value.
By using these resources and strategies, beginners can build confidence and continue their automation journey with strong support.
Starting with one simple automation helps organizations build confidence and achieve long-term success. The table below highlights why this approach works:
Approach | Description |
|---|---|
Incremental Approach | Simple tasks allow teams to learn and celebrate early wins. |
Continuous Improvement | Small victories encourage ongoing enhancements. |
Structured Planning | Clear goals and resources support employee confidence and performance. |
Business process automation offers many benefits, including increased efficiency, cost savings, and improved accuracy. Teams that celebrate small wins boost morale, maintain momentum, and foster learning opportunities. Regular recognition of achievements creates a positive culture and increases motivation. For those interested in learning more or seeking support with systems and teams, reaching out can provide valuable guidance on the next steps.
FAQ
What is business process automation?
Business process automation uses technology to complete tasks with little human help. Companies use it to make work faster, reduce mistakes, and save money.
Which business tasks are best for automation?
Repetitive tasks that follow clear steps work best. Examples include data entry, scheduling, sending emails, and updating records. These tasks often slow teams down when done by hand.
Do small businesses benefit from automation?
Yes. Small businesses can save time and reduce errors by automating simple tasks. Automation helps them compete with larger companies and focus on growth.
Is coding required to automate business processes?
Most popular automation tools do not require coding. Platforms like Zapier and Power Automate use visual interfaces. Users can build workflows by dragging and dropping actions.
How can a company choose the right automation tool?
A company should compare features, ease of use, integration options, and price. Testing a free trial helps teams see if the tool fits their needs.
What risks come with automation?
Automation can create security risks and compliance issues. Companies must use strong access controls, monitor workflows, and train employees to keep data safe.
How long does it take to see results from automation?
Many companies notice improvements within a few weeks. Time savings and fewer errors often appear soon after launching the first automated workflow.
Can automation replace employees?
Automation handles repetitive work, not creative or complex tasks. Employees can focus on higher-value activities. Most companies use automation to support, not replace, their teams.



