Automate Business Processes Without Coding

Yes, businesses can automate business processes without coding. Many organizations now use no-code automation tools to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Recent surveys show that automation boosts productivity, strengthens operational effectiveness, and minimizes errors. Over 80% of businesses in the United States rely on these solutions to fill technical gaps and support business management needs. Teams in sales and other departments gain more time for tasks that require specialized knowledge. No-code platforms make automation accessible for everyone.
Key Takeaways
No-code automation tools allow businesses to streamline processes without needing coding skills.
Automation boosts efficiency by reducing repetitive tasks, enabling employees to focus on higher-value work.
Companies can save costs significantly by automating processes, often breaking even within a year.
Standardized workflows through automation minimize errors and ensure consistent results.
Small businesses can compete effectively by automating tasks like invoicing and customer communication.
Choosing the right no-code platform involves considering integration capabilities, user experience, and security features.
Regular monitoring and updates of automated workflows help maintain efficiency and adapt to changing needs.
Involving employees in the automation process and providing training enhances adoption and long-term success.
Why Automate Business Processes
Automating business processes brings many advantages to organizations of all sizes. Companies use automation to streamline daily operations, allowing employees to focus on higher-value tasks. Business process automation standardizes workflows, ensuring that every critical step happens in the right order. This approach leads to consistent results and fewer mistakes.
Benefits
Efficiency
Automation improves efficiency by removing bottlenecks and speeding up production. Employees no longer need to spend hours on repetitive tasks. Instead, they can dedicate their time to creative problem-solving and customer service. Automation also helps companies scale their operations without hiring more staff.
Tip: Automating routine tasks frees up time for employees to work on projects that require human judgment and expertise.
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Enhanced Efficiency | Streamlines operations, eliminating bottlenecks and speeding up production. |
Scalability | Allows businesses to grow without proportional increases in staff or resources. |
Employee Productivity | Employees can focus on more meaningful work instead of routine tasks. |
Cost Savings
Companies often see significant cost reductions after they automate business processes. Automation lowers labor costs by reducing the need for manual work. Many organizations report breaking even within a year of implementing automation.
Industry/Function | Cost Savings Percentage |
|---|---|
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | 25–50% |
Manufacturing | Up to 40% |
Logistics | Up to 30% |
Automated Customer Service | Up to 60% |
Average savings of $10-15 per invoice in accounts payable after automation.
88% of organizations report improved efficiency and reduced labor costs.
Error Reduction
Automation ensures that processes run the same way every time. This consistency reduces the risk of human error and leads to more accurate results. Standardized workflows help companies avoid costly mistakes and improve overall quality.
Note: Automation helps standardize processes, ensuring that critical steps are not missed and consistent outcomes are achieved.
Who Should Automate
Small Businesses
Small businesses benefit from automation by saving time and money. They can compete with larger companies by using automation to handle tasks like invoicing, scheduling, and customer communication. Automation allows small teams to do more with fewer resources.
Teams
Teams in departments such as HR, operations, and customer service see major improvements from automation. Workflow automation supports multi-step processes in industries like healthcare, banking, and insurance. Teams can collaborate more effectively and deliver better results.
Type of Automation | Description | Industries Benefiting |
|---|---|---|
Workflow Automation | Multi-step processes | HR, Operations, Healthcare, Construction, Banking, Insurance |
Robotic Process Automation | High volume tasks | Manufacturing, Industrial-heavy industries |
Intelligent Automation | Cognitive, adaptive tasks | Data-heavy industries |
Automate business processes to achieve greater efficiency, cost savings, and accuracy. These benefits help organizations grow and adapt in a competitive market.
No-Code Tools

No-code automation platforms have transformed how organizations manage daily operations. These tools allow users to automate business processes without writing code. Many companies now rely on these platforms to save time and reduce manual work.
Automation Platforms
Workflow Tools
Several no-code platforms stand out for their ability to streamline workflows.
Zapier connects thousands of apps and suits small businesses and startups.
IFTTT offers simple personal automations and supports over 1,000 apps.
Parabola provides strong data processing features, ideal for retail and logistics.
Make delivers advanced workflow capabilities for SaaS and data-driven companies.
Tray.ai supports enterprise-grade automation with scalability and governance.
n8n gives teams flexible, self-hosted options for complex needs.
Many users choose these platforms for their intuitive interfaces and wide range of integrations.
Integration Options
Integration is a key feature of no-code tools. Zapier and Make offer affordable pricing and connect with hundreds of applications. Parabola excels in data-heavy industries, while Tray.ai provides AI-ready integrations for large enterprises. n8n allows complete control through self-hosting. These platforms help organizations automate business processes across departments, from marketing to finance.
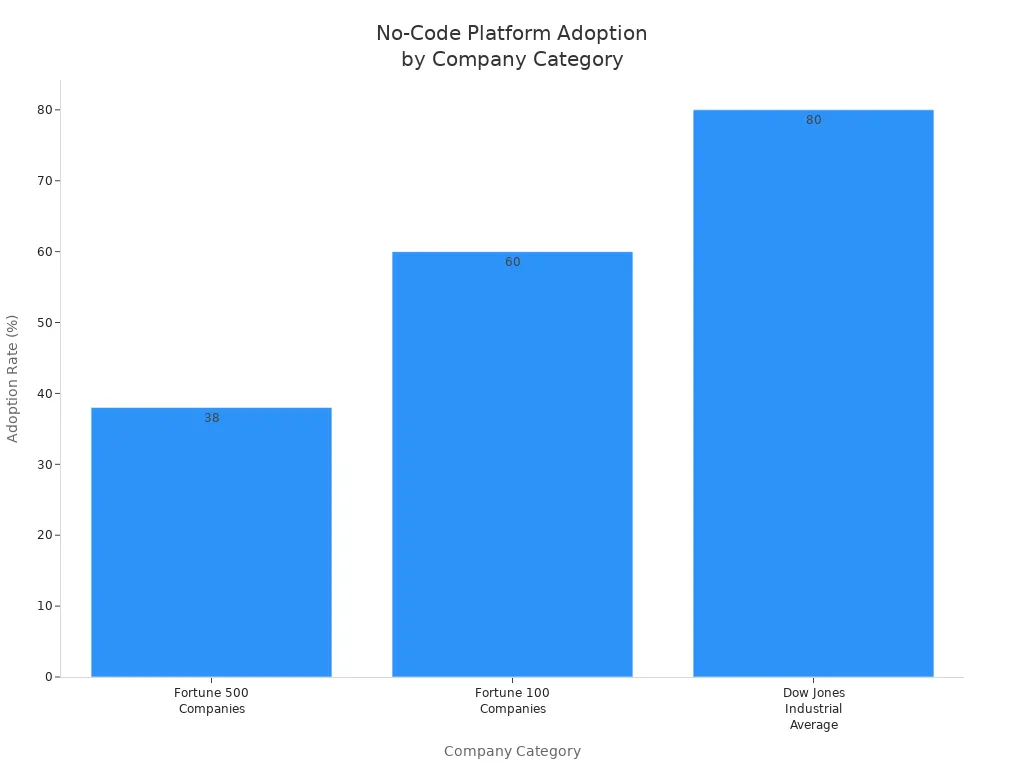
Company Category | Adoption Rate | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
Fortune 500 Companies | 38% | 2021 | |
Fortune 100 Companies | 60% | 2021 | |
Dow Jones Industrial Average | 80% | 2021 | |
Global Low-Code Market | $187 billion | 2030 |
Choosing a Tool
Features
Selecting the right no-code platform depends on several factors.
Pre-built connectors allow users to link many applications quickly.
Drag-and-drop interfaces make it easy for non-technical staff to build workflows.
API-led integrations support more advanced automation needs.
Enterprise-grade governance and security features protect sensitive data.
Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
Integration Capabilities | The tool should support a wide range of pre-built connectors for various applications. |
Security | Strong encryption and role-based access controls are essential to protect sensitive data. |
Scalability | The platform should be able to grow with the business and handle enterprise-scale operations. |
User Experience | An intuitive interface with features like drag-and-drop functionality enhances usability. |
Business Agility | The tool should allow for quick modifications to automations to meet evolving business needs. |
Subject Matter Expertise | Empowering business teams to decide which processes to automate ensures relevance and efficiency. |
Tip: Teams should review platform features and integration options before making a decision.
Compatibility
Compatibility matters when choosing a no-code tool. The platform must work with existing software and support future growth. Security and scalability remain important for organizations handling sensitive information or large volumes of data. Business agility helps companies adapt quickly to new challenges.
No-code platforms enable organizations to automate business processes efficiently. These tools offer flexibility, strong integration, and user-friendly design, making automation accessible to everyone.
Automation Steps
Automating business processes with no-code tools involves a clear, step-by-step approach. This section explains how organizations can identify, map, build, and test automated workflows for better efficiency.
Identify Processes
Repetitive Tasks
The first step is to review daily tasks. Teams should analyze their workflows to spot activities that occur often. These tasks usually follow a set pattern and take up valuable time. Examples include:
Employee expense management, which tracks and reimburses expenses without manual entry.
Social media management automation, which schedules posts and monitors engagement.
Daily or frequent tasks, such as sending reminders or updating spreadsheets.
Rule-based processes, like sorting emails or assigning tickets.
Error-prone tasks, where manual work leads to mistakes.
Time-consuming processes, such as data entry or report generation.
Tip: Focus on tasks that are frequent, rule-based, or take up a lot of staff hours. These offer the biggest gains from automation.
Areas for Improvement
After listing repetitive tasks, teams should look for areas that need improvement. They can ask questions like: Which tasks slow down the workflow? Where do errors happen most often? For instance, automating lead management can move leads from Facebook Ads directly into a CRM. Integrating Trello with QuickBooks can speed up invoice creation and reduce administrative work.
Map Workflows
Inputs and Outputs
Mapping a workflow helps teams understand each step in a process. Creating a visual workflow diagram outlines every action from start to finish. This method brings clarity and shows how different steps connect. Teams can use flowcharts, swimlane diagrams, or SIPOC diagrams to visualize the process.
Mapping Technique | Description |
|---|---|
Fundamental Flowchart | Basic process flow representation |
Workflow Diagram | Visualizes workflow steps |
Swimlane Mapping | Shows who does what in a process |
SIPOC Diagram | Outlines Suppliers, Inputs, Processes, Outputs, Customers |
Triggers and Actions
Every automated workflow needs a trigger and an action. A trigger starts the process, such as receiving a new email or form submission. The action is what happens next, like sending a response or updating a database. No-code tools let users set up these triggers and actions with simple selections.
Triggers: New email, form submission, file upload
Actions: Send notification, update record, create invoice
Note: Process mapping clarifies how different steps intersect and simplifies complex workflows. It also helps teams evaluate current processes for future improvements.
Build and Test
Drag-and-Drop Setup
No-code platforms use visual tools to build workflows. Users can drag and drop components, such as triggers, actions, and conditions, onto a canvas. This setup removes the need for programming skills. Core components include workflow builders, connectors, and variables.
Drag a trigger (like "new email received") onto the workflow.
Add actions (such as "send auto-reply" or "save attachment").
Use connectors to link different apps or services.
Testing
Testing ensures the automation works as planned. Teams should run the workflow with sample data and check each step. They can tweak parts of the workflow and test changes quickly. Best practices include:
Implement error handling to catch mistakes during automation.
Maintain logs to track performance and spot issues.
Avoid trying to automate everything at once. Start with the most impactful tasks.
Involve all stakeholders in the testing phase to ensure the workflow meets business needs.
Common mistakes to avoid: Automating a process that does not work manually, skipping error handling, and not giving enough time to testing.
Organizations that follow these steps can automate business processes efficiently. They gain more control, reduce errors, and free up time for higher-value work.
Optimization Tips
Optimizing automated business processes helps organizations maintain efficiency and adapt to changing needs. Teams can use several strategies to monitor, update, and secure their workflows. Business process management (BPM) encourages ongoing evaluation and improvement.
Monitor
Performance
Teams should track key metrics to measure the success of automated workflows. Monitoring these indicators helps identify strengths and areas for improvement.
Quality: The output meets client standards and internal quality checks.
Error rate: The number of failed units during each process cycle.
Customer satisfaction: The process meets customer expectations.
Conversion rate: The number of prospects who become customers.
Competitiveness: Market share compared to other companies.
Profitability: The relationship between revenue and costs.
Cycle time reduction: The speed of the process after automation.
Better productivity: Improvements in output and efficiency.
Regular monitoring ensures that automation delivers consistent results and supports business goals.
Troubleshooting
When issues arise, teams should investigate the root cause. They can review error logs, analyze failed steps, and adjust workflows as needed. Quick troubleshooting prevents disruptions and keeps processes running smoothly.
Update
Reviews
Organizations benefit from regular workflow reviews. Audits help identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. Teams can gather feedback from employees to understand which steps need updates.
Perform quarterly workflow audits.
Collect feedback from staff about workflow challenges.
Map workflows to understand dependencies and bottlenecks.
Adaptation
Adapting workflows keeps automation relevant. Teams can implement changes through planned iterations. Leveraging AI and machine learning can make automation smarter and more responsive. Seamless integration across systems maintains workflow efficiency.
Continuous improvement supports long-term success and helps organizations stay competitive.
Security
Data Privacy
Protecting data is essential in automated workflows. No-code automation tools streamline the process of fulfilling Data Subject Requests (DSRs), which supports data privacy compliance. These tools reduce manual effort, improve accuracy, and respect user permissions across different systems. Customizable workflows allow businesses to meet specific privacy needs and manage consumer data according to preferences.
Permissions
Strong security features safeguard sensitive information. The following table highlights important security considerations:
Security Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Only authorized users can access specific functions and data. | |
Data Encryption | Sensitive data stays protected during storage and transmission. |
Audit Logs | User activities and changes are tracked for accountability. |
User Training | Users learn security best practices to prevent vulnerabilities. |
Regular Security Assessments | Periodic evaluations identify and fix vulnerabilities. |
Governance Policies | Clear guidelines control who can create and modify automations. |
Organizations should also comply with standards such as HIPAA, GDPR, ISO 27001, SOC 2, NIST, and FedRAMP. These frameworks help maintain data privacy and security in automated workflows.
Security and privacy must remain a top priority when automating business processes.
Challenges
Automating business processes with no-code tools brings many benefits, but organizations often face several challenges. Understanding these obstacles helps teams plan better and achieve smoother automation.
Integration Limits
Unsupported Apps
No-code platforms connect with many popular apps, but some applications remain unsupported. Teams may struggle to automate workflows that involve legacy systems or specialized third-party services. Integration with older IT infrastructure can be difficult, especially when those systems lack standard APIs.
Some platforms cannot handle complex logic or highly customized workflows.
Performance issues may occur when processing large volumes of data.
Pre-built connectors may not cover every business need.
Teams should review their current software stack before choosing a no-code platform.
Workarounds
When direct integration is not possible, teams can use several workarounds:
Use API integrations if available, allowing custom connections between systems.
Develop a comprehensive data migration plan to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Choose platforms that offer flexibility and support for custom scripts or webhooks.
Work with vendors who provide strong customer support and clear service agreements.
Careful planning and performance testing help manage technical challenges and avoid disruptions.
Scaling
Volume
As businesses grow, automated workflows must handle more data and users. Many no-code platforms face scalability issues due to their design or underlying technology. High data volumes can lead to errors or slow performance.
Test systems under higher loads to find stress points.
Monitor automation return on investment to ensure continued value.
Complexity
Business processes often become more complex over time. No-code tools may struggle with advanced logic or multi-step workflows. Vendor lock-in can also limit flexibility, making it hard to switch platforms or expand integrations.
Gradually introduce advanced automation as processes evolve.
Create workflows with role-based access controls for new team members.
Ensure seamless integration with new systems as the business changes.
Adoption
Training
Employees may find no-code automation tools challenging if they lack technical experience. Training and change management play a key role in successful adoption.
Step | Description |
|---|---|
1 | |
2 | Select user-friendly tools that integrate well. |
3 | Ensure smooth data syncing with existing systems. |
4 | Develop onboarding checklists for organization. |
5 | Provide hands-on training and ongoing support. |
6 | Measure success with clear metrics. |
Personalization and feedback improve retention and engagement.
Automation saves time, enhances experiences, and improves compliance.
Usage
Barriers to adoption include technical complexities and a lack of understanding of programming concepts. Teams should involve employees early, provide comprehensive training, and highlight how automation supports their work.
Barrier Description | Source |
|---|---|
Technical complexities that require a programming mindset | Rokis and Kirikova (2022) |
Lack of understanding of programming concepts | Luo et al. (2021) |
Need for comprehensive training and change management | Sahay et al. (2020) |
Involving employees from the start and offering clear career paths for automation skills can boost adoption and long-term success.
Success Stories
Small Business
Time Saved
Small businesses often face challenges with limited resources and staff. Many owners look for ways to save time on daily tasks. No-code automation helps these businesses reduce hours spent on administrative work. Systems and teams that use automation tools can focus more on strategic activities. For example, automated invoicing and scheduling allow staff to spend less time on paperwork and more time serving customers.
Automation gives small business teams the ability to handle more work without increasing headcount.
The following table shows measurable outcomes that small businesses have achieved through no-code automation:
Outcome | Description |
|---|---|
Automation reduces time spent on administrative tasks, allowing focus on strategic activities. | |
Improved output | Consistent automation leads to predictable and repeatable results in business processes. |
Consistent quality | Automation ensures that each task is completed to the same standard, enhancing reliability. |
Better client experiences | Prompt responses through automation improve client satisfaction and engagement. |
Reduced cost | Decreased labor costs for repetitive tasks contribute to overall savings for the business. |
Data-driven insights | Analytics from automation tools help identify bottlenecks and improve processes. |
Growth
Growth becomes possible when small businesses automate their processes. Teams can scale operations without hiring more employees. Automated systems help manage higher volumes of work, such as processing orders or handling customer requests. Many businesses report that automation leads to better client experiences and more consistent results. Data-driven insights from automation tools also help owners make smarter decisions about future growth.
Team Productivity
Collaboration
Teams in larger organizations benefit from automation by improving collaboration. Systems that automate workflows allow team members to share information quickly and work together more efficiently. For example, automated notifications keep everyone updated on project status. Standardized processes help teams avoid confusion and reduce errors.
Automated workflows encourage teams to communicate and solve problems together.
Manual Work Reduction
Reducing manual work remains a key goal for many teams. Automation tools handle repetitive tasks, such as data entry or form processing. This shift allows employees to focus on creative and complex work. Documented case studies show that systems and teams using automation have saved thousands of hours and cut onboarding time in half.
The table below highlights improvements in team productivity from business process automation:
Organization | Improvement | Description |
|---|---|---|
AllMed | Automated web forms streamlined workflows, significantly reducing manual work and costs. | |
Unknown | Onboarding time halved | Automated workflows cut onboarding time from four weeks to two. |
Salesforce | Enhanced client onboarding | Implemented workflows to standardize processes, reduce errors, and improve collaboration. |
Systems and teams that adopt automation experience better collaboration, fewer mistakes, and more time for valuable work. These real-world examples show how business process automation leads to measurable improvements in efficiency and growth.
Get Started
Starting business process automation without coding requires a clear plan and the right resources. Teams can follow a simple checklist to begin their journey and access helpful tools and communities for ongoing support.
Quick Checklist
Sign Up
Businesses should begin by choosing a no-code automation platform that fits their needs. Popular options include Zapier, Make, and Trello. Signing up for a free trial or basic account allows teams to explore features and test integrations.
Select a no-code tool such as Zapier, Make, or Trello.
Create an account using a business email.
Review available templates and connectors.
Tip: Many platforms offer free versions for small teams to experiment with basic workflows.
Choose Workflow
Identifying the right process to automate is essential. Teams should look for repetitive tasks that take up valuable time. Examples include automating lead management, scheduling, or invoice creation. Documenting current workflows helps pinpoint areas for improvement.
List daily tasks that repeat often.
Analyze workflows to find bottlenecks.
Ask questions about each process to prioritize automation.
For instance, automating the transfer of leads from Facebook Ads to a CRM system saves hours each week. Linking Trello completions to QuickBooks streamlines invoice generation and reduces administrative work.
Test
Testing ensures that the automation works as expected. Teams should run sample workflows and check each step for accuracy. Adjustments may be needed to improve results or fix errors.
Set up a test workflow using sample data.
Monitor each step for correct execution.
Make changes based on feedback and results.
Note: Start with one workflow and expand as the team gains confidence.
Resources
Tutorials
Many platforms provide step-by-step tutorials to help users get started. These guides cover basic setup, workflow creation, and troubleshooting. Teams can learn how to automate tasks using tools like Quixy, Notion, Budibase, and Airtable.
Platform | Tutorial Type | Skill Level |
|---|---|---|
Zapier | Video & written | Beginner |
Make | Interactive guides | Beginner |
Trello | Task management tips | Beginner |
Airtable | Database automation | Intermediate |
Tutorials help teams build skills and solve common problems quickly.
Community
Joining a user community provides ongoing support and inspiration. Many platforms host forums, webinars, and online groups where users share ideas and solutions. Communities for tools like Webflow, Shopify, Stripe, and Retool offer advice and best practices.
Ask questions and get answers from experienced users.
Share workflow templates and automation tips.
Stay updated on new features and integrations.
Community support helps teams overcome challenges and discover new ways to automate processes.
Ready to automate your business processes? Reach out to our team for guidance and resources. Teams can start small, learn quickly, and unlock new levels of efficiency with no-code automation.
Automating business processes without coding offers lasting advantages. Organizations gain cost efficiency, better productivity, and improved compliance. No-code platforms allow employees to manage workflows easily and scale operations as needs grow.
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Cost Efficiency | |
User-Friendliness | Enables staff to automate tasks without coding. |
Scalability | Supports growth and complex workflows. |
Experts recommend starting with a simple workflow to build confidence. Teams should develop training programs and monitor performance for continued success. Ongoing learning helps organizations adapt and maximize results as they automate business processes.
FAQ
What is a no-code automation tool?
A no-code automation tool lets users create automated workflows without programming knowledge. These platforms use visual interfaces, such as drag-and-drop builders, to connect apps and set up processes.
Can teams automate processes without IT support?
Teams can automate many business tasks using no-code platforms. Most tools offer simple interfaces and templates. Employees do not need help from IT for basic workflows.
Which business processes work best for automation?
Repetitive tasks, such as data entry, scheduling, and email responses, work best for automation. Teams often automate processes that follow clear rules and occur frequently.
Are no-code tools secure for sensitive data?
Most no-code platforms include security features like encryption and role-based access controls. Teams should review each tool’s compliance with standards such as GDPR or HIPAA.
How much does no-code automation cost?
Pricing varies by platform. Many tools offer free plans for small teams. Paid plans usually depend on the number of workflows, integrations, or users.
Can no-code automation scale with business growth?
No-code platforms support scaling for most small and medium businesses. Larger organizations may need enterprise features, such as advanced integrations and governance controls.
What happens if an app is not supported?
If a platform does not support an app, teams can use workarounds like API integrations or webhooks. Some platforms allow custom connectors for added flexibility.
How can employees learn to use no-code tools?
Most platforms provide tutorials, guides, and community forums. Employees can start with basic workflows and build skills through practice and online resources.



