How to Map and Optimize Business Processes for Better Results
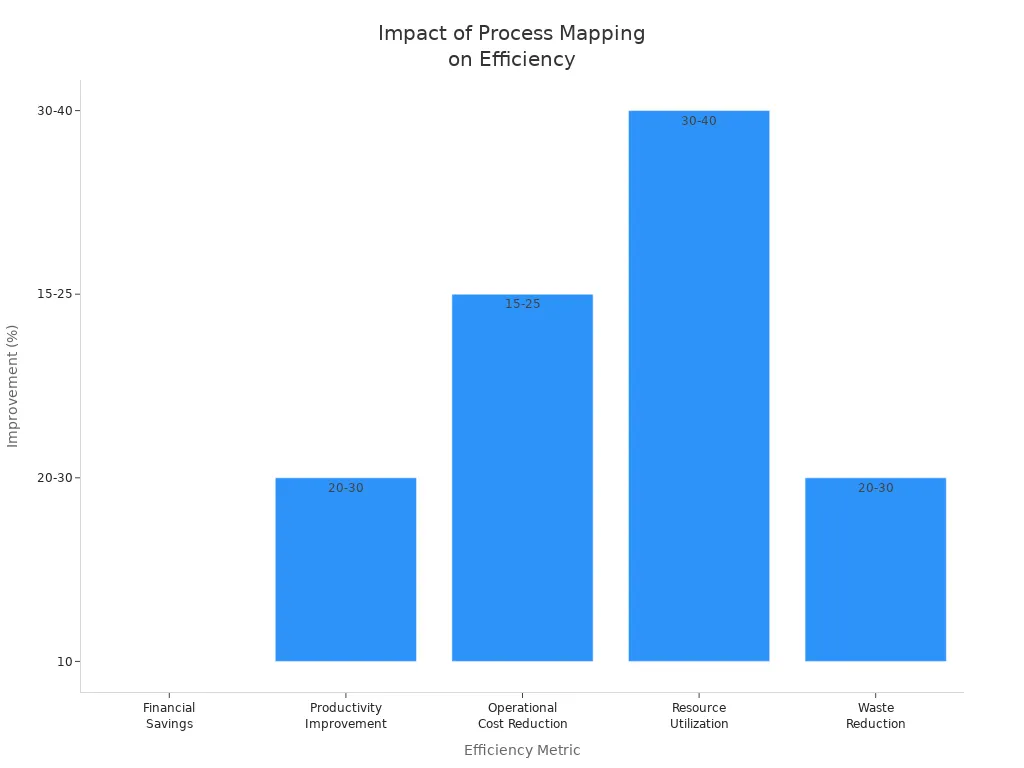
Mapping and optimizing business processes delivers measurable gains in efficiency, productivity, and outcomes for organizations of any size. Companies often see a 20-30% boost in productivity and up to a 25% reduction in operational costs after refining their processes. The following table highlights key improvements:
Statistic | Impact |
|---|---|
Significant financial savings | |
20-30% productivity improvement | Higher operational efficiency |
15-25% reduction in operational costs | Resource optimization leads to cost savings |
30-40% improvement in resource utilization | Better management of Resources |
20-30% decrease in waste | Less waste through streamlined Systems |
Organizations that use a clear Methodology for process mapping also report faster task completion and higher customer satisfaction. Readers can reflect on how their current approach compares and consider the potential for positive change.
Key Takeaways
Mapping business processes can boost productivity by 20-30% and reduce operational costs by up to 25%.
Identifying core processes is essential for effective business process mapping and optimization.
Clear objectives guide successful business process management initiatives and help teams stay focused.
Regular reviews of processes help identify inefficiencies and support continuous improvement.
Assigning clear roles and responsibilities prevents confusion and enhances accountability in teams.
Utilizing automation technologies can streamline repetitive tasks and improve overall efficiency.
Standardizing processes leads to consistent results and enhances customer satisfaction.
Measuring success through specific metrics helps organizations track progress and make informed decisions.
Business Processes Overview
What Are Business Processes
Business processes shape how organizations achieve their goals. Leading business management sources describe these processes in similar ways. The table below shows how different experts define them:
Source | Definition |
|---|---|
Processology | |
TechTarget | A business process is an activity or set of activities that accomplish a specific organizational goal. |
TechTarget | A business process is a series of related tasks that result in a desired output; it is an established set of repeatable activities. |
These definitions highlight that business processes involve a sequence of steps or activities. Each process aims to deliver a clear result, whether that means serving a customer, producing a product, or supporting internal operations.
Types of Processes
Organizations rely on several types of processes to function smoothly. Each type plays a unique role in supporting business goals.
Core Processes
Core processes create value for customers and drive revenue. These processes include product development, sales, and service delivery. They form the backbone of any organization. Without strong core processes, a company cannot deliver on its promises or compete in the market.
Support Processes
Support processes make value delivery possible. These activities serve internal needs, such as IT support, human resources, and accounting. Support processes do not directly generate revenue, but they ensure that core processes run without interruption.
Management Processes
Management processes guide and monitor business operations. These processes include planning, budgeting, and performance reviews. They help leaders set direction and measure progress. Management processes ensure that the organization stays on track and meets its objectives.
Strategic Processes
Strategic processes focus on long-term goals and direction. These processes involve setting the overall strategy, analyzing the market, and making high-level decisions. Strategic processes help organizations adapt to change and stay competitive.
Tip: Understanding the different types of processes helps leaders assign resources and attention where they matter most.
Why Processes Matter
Well-designed processes give organizations a competitive edge. The following points show why processes play a critical role:
Streamlined processes increase efficiency and reduce time-to-market.
Regular reviews help identify and remove inefficiencies, lowering costs.
Clear processes support business growth and maintain quality.
Improved processes enhance customer experiences and loyalty.
Employees understand their roles better, leading to higher engagement and less confusion.
Organizations that invest in business processes see better operational results and stronger alignment with their strategy. Every process, from core to strategic, contributes to overall success.
Business Process Management Basics
Business process management helps organizations design, monitor, and improve their business processes. This approach ensures that every process aligns with company goals and delivers measurable results. Companies that use business process management often see better efficiency, higher quality, and improved customer satisfaction.
Stages of Business Process Management
Business process management includes several stages. Each stage plays a key role in process improvement and helps organizations achieve better outcomes.
Planning
During planning, teams identify current business processes and set goals for improvement. They document each process and decide which areas need change. Planning ensures that every process supports business objectives.
Execution
Execution brings planned processes to life. Teams assign tasks, follow mapped workflows, and monitor initial performance. This stage tests how well new processes work in real situations.
Control
Control involves tracking performance metrics and making sure processes function as intended. Teams use data to spot problems and measure progress. Control helps organizations maintain consistency and quality.
Optimization
Optimization focuses on continuous process improvement. Teams analyze feedback and performance data to find new ways to make processes more efficient. They update workflows and remove bottlenecks. Optimization leads to better results over time.
Note: The following table shows the main stages of business process management and their descriptions.
Stage | Description |
|---|---|
Design | Identifies current processes and plans improvements that align with business goals. |
Model | Maps and tests workflows under different scenarios to introduce efficiencies. |
Execute | Brings planned workflows to life by assigning tasks and monitoring initial performance. |
Monitor | Involves tracking performance metrics to ensure processes are functioning as intended. |
Optimize | Focuses on continuous improvement of processes based on performance data and feedback. |
Key Benefits
Organizations that manage their business processes effectively gain several advantages. The following table highlights the key benefits:
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity | Automating routine tasks reduces manual intervention, allowing focus on higher-value activities. |
Cost Savings | Optimizing processes reduces costs and waste while increasing productivity. |
Improved Quality and Consistency | Mapping processes helps identify areas for improvement, ensuring tasks are executed consistently. |
Agility and Flexibility | BPM allows quick adaptation to market changes through efficient workflows. |
Enhanced Visibility and Transparency | Real-time insights into processes improve communication and reduce information silos. |
Compliance and Risk Management | Automating compliance helps avoid fines and mitigate potential risks. |
Customer Satisfaction | BPM improves response times and communication, leading to increased customer loyalty. |
Recent studies show that business process management leads to measurable improvements. Customer satisfaction rates can rise from 60% to 90%. Process errors, such as those in invoice production, can be eliminated. The acceptance rate of first offers may increase from 65% to 95%. Time to issue permits can drop by 50%. These results show that process improvement delivers real value.
Business processes often connect with other processes. For example, launching a project implementation has a very strong correlation with scheduling, management of materials, and production. Improving one process can strengthen others and boost overall performance.
Tip: Documenting processes and tracking key performance indicators help organizations achieve measurable outcomes. These outcomes include higher customer satisfaction and fewer errors, which are critical for success.
Mapping Core Processes
Identifying Core Processes
Organizations must first identify which processes drive the most value. This step lays the foundation for effective business process mapping. Leaders can use a structured approach to pinpoint these essential workflows:
List major business functions. Common areas include Sales, Marketing, Human Resources, Operations, and Finance.
Apply the 80/20 rule. Focus on the processes that create the most impact for the organization.
Assign ownership. Each function should have a clear owner who takes responsibility for documentation and improvement.
Name each process clearly. Use consistent, high-level names to avoid confusion.
By following these steps, teams ensure they focus on the processes that matter most. This approach supports business process management and helps organizations allocate resources efficiently.
Mapping Steps
Once core processes are identified, teams can begin business process mapping. This method creates a visual representation of how work flows through the organization. The following steps guide teams through the mapping process:
Ideate and plan. Gather a team and clarify the vision for future success. Ask questions such as, "What does success look like?"
Form a cross-functional team. Include members from different departments to capture a range of perspectives and ensure clear communication.
Analyze current workflows. Use flowcharts or digital tools to map existing processes. Identify redundancies and collect performance data.
These steps help teams understand how processes interact and where improvements can be made. Streamlined processes often emerge from this analysis, leading to better efficiency and fewer errors.
Tip: Involving people from multiple departments uncovers hidden challenges and ensures the mapped processes reflect real-world operations.
Tools for Mapping
Business process mapping tools play a key role in visualizing and improving processes. These tools help teams illustrate how work moves across departments, highlight decision points, and clarify each step involved. The most widely used tools offer several advantages:
User-friendly interfaces with drag-and-drop features and pre-made templates.
Real-time collaboration, including simultaneous editing and in-app chat.
Customization options for different diagram types and business needs.
Integration with existing business systems for smooth data flow.
Powerful visualization features for creating clear, professional diagrams.
Popular tools for business process mapping include:
Creately
Lucidchart
MindMeister
Pipefy
ClickUp
EdrawMax
Microsoft Visio
GitMind
Canva
Cacoo
Visme
Notion
Smartsheet
Miro
Monday.com
Lucidchart stands out for its collaborative features, allowing multiple users to work on diagrams at the same time. SmartDraw offers a simple drag-and-drop interface and a wide range of templates. Edraw Max provides comprehensive collaboration tools and various export options.
Selecting the right tool depends on the organization's needs and the complexity of its processes. Effective business process mapping leads to better understanding, improved communication, and more efficient operations.
Setting Goals and Planning
Defining Objectives
Clear objectives guide every successful business process management initiative. Teams that set specific goals can make better decisions and allocate resources more effectively. Objectives give direction and help everyone understand what the organization wants to achieve. Without clear objectives, projects often lose focus and struggle to deliver results.
Leaders should communicate objectives to all stakeholders. This ensures that everyone understands the purpose and desired outcomes. Teams benefit from setting a range of goals—short-term, medium-term, and long-term. Short-term goals help track immediate progress. Medium-term goals keep the project on course. Long-term goals align with the overall vision of the organization.
Note: Specific and measurable objectives allow teams to track progress and celebrate achievements. Realistic goals consider available resources and possible constraints. This clarity keeps everyone motivated and focused on timely task completion.
A table can help teams organize their objectives:
Goal Type | Example Objective | Time Frame |
|---|---|---|
Short-term | Reduce process errors by 10% | 3 months |
Medium-term | Improve customer response time by 20% | 6-12 months |
Long-term | Achieve industry-leading process efficiency | 2-3 years |
Teams that define objectives at the start of a project can measure success more easily. This approach supports alignment with organizational priorities and helps maintain momentum.
Process Scope
Defining the scope of processes is a critical step in planning. Scope outlines what the team will include and exclude from the improvement effort. A clear scope prevents confusion and keeps the project manageable.
Teams should start by identifying the boundaries of each process. They can ask questions such as, "Where does this process begin and end?" and "Which departments or roles participate?" This step ensures that everyone understands the limits of the project.
A well-defined scope helps teams avoid scope creep. Scope creep happens when new tasks or requirements get added without proper review. This can delay progress and increase costs. By setting clear boundaries, teams can focus on the most important processes and deliver results faster.
A checklist can help teams define process scope:
Identify the start and end points of the process.
List all participants and stakeholders.
Specify what the process will and will not include.
Confirm alignment with business goals.
Business processes often overlap with other workflows. Teams should document these connections to avoid gaps or duplication. This approach supports better communication and smoother handoffs between teams.
Tip: Reviewing the scope regularly helps teams stay on track and adjust to changes in business needs.
Setting clear objectives and defining process scope lay the foundation for effective business process management. These steps ensure that teams work toward meaningful goals and focus their efforts where they matter most.
Assigning Roles and Execution
Assigning Responsibilities
Clear roles and responsibilities form the backbone of successful processes. When teams know who does what, they avoid confusion and delays. Many organizations use frameworks to assign roles in business processes. The RACI model is one of the most popular. It stands for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed. The table below explains each role:
Role | Description |
|---|---|
Responsibility | For performing the process or task |
Accountability | Authority for the results achieved by the process or task |
Consulted | The roles that have the information required for successful completion |
Informed | The roles that need to receive notification that the task or process was completed |
Another helpful approach is the RAPID framework. Developed by Bain Consulting, RAPID addresses unclear roles in decision-making. It assigns specific roles to each step, which leads to better performance and stronger results. The RAPID roles include:
Input: The person who provides information for the decision.
Recommend: The individual who suggests a course of action.
Agree: The person who must agree before moving forward.
Decide: The individual who makes the final decision.
Perform: The person responsible for executing the decision.
These frameworks help teams clarify expectations and reduce overlap. Leaders should match each process step to a role. This practice supports workflow management and ensures accountability. When everyone understands their part, processes run smoothly and deliver better outcomes.
Tip: Assigning clear roles at the start of a project prevents confusion and builds trust among team members.
Communication
Strong communication keeps processes on track and teams aligned. Companies that excel in communication often see higher success rates in process execution. Several strategies help organizations communicate effectively:
Consistent messaging ensures everyone receives the same information. Coca-Cola’s ‘Share a Coke’ campaign used this approach to create a unified experience.
Two-way communication encourages feedback and dialogue. Zappos uses regular meetings and internal platforms to foster open discussion.
Tailored communication adapts messages for different groups. This helps each audience understand their role in the process.
Using multiple channels, like Salesforce, reaches more people and fits different preferences.
Visual aids and storytelling make complex processes easier to understand and remember.
Training and support equip leaders and teams with the skills to communicate well. IBM invests in continuous learning for this reason.
Monitoring and adapting communication, as Google does with Objectives and Key Results, keeps everyone aligned and transparent.
Celebrating milestones, as seen at Microsoft, boosts morale and reinforces progress.
Note: Good communication is not just about sending messages. It also means listening, adapting, and making sure everyone feels included.
Teams that combine clear roles with strong communication see the best results. These practices help organizations manage processes, avoid mistakes, and achieve their goals.
Process Optimization

Business Process Automation
Business process automation transforms how organizations operate. Teams use technology to handle repetitive tasks, freeing people to focus on higher-value work. Systems play a key role by connecting data, workflows, and communication across departments. Teams that embrace automation see faster results and fewer errors.
Today, several impactful business process automation technologies help organizations achieve efficient business process outcomes:
Process mining uses real data to visualize workflows and uncover inefficiencies. Teams can spot bottlenecks and identify where automation will have the most impact.
Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) converts unstructured data into usable formats. This technology uses OCR, NLP, and machine learning to improve accuracy in document handling.
Virtual agents and chatbots automate customer interactions. These tools provide quick answers and personalized service, improving customer satisfaction.
Data pipeline automation manages data flow across systems. This is essential for real-time decision-making and supports AI integration.
Hyperautomation platforms combine robotic process automation (RPA), AI, and analytics. These platforms enable large-scale automation across multiple departments.
Low-code and no-code tools allow non-developers to create applications and workflows. Teams can automate processes quickly without waiting for IT support.
Many organizations have achieved measurable improvements through business process automation. The following table highlights real-world examples:
Case Study | Industry | Improvement | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
National Bank of Abu Dhabi | Banking | ||
Caixabank | Banking | IT Service Management improved by 80% | |
Colorado Community College System | Education | Saved 40 hours a week | |
Bernstein AG | Manufacturing | Reduced customer product request time from weeks to days | |
If Latvia | Insurance | Reduced claims processing from 10 days to 15 hours |
These examples show how systems and teams work together to optimize business processes. For instance, the National Bank of Abu Dhabi used automation to speed up loan approvals. Their teams collaborated with IT to redesign workflows and connect systems, resulting in faster service for customers.
Tip: Start with small automation projects. Involve cross-functional teams to ensure the solution fits real business needs.
Standardization
Process standardization creates a foundation for consistent and reliable results. Teams document best practices and set clear guidelines for each step. Systems help enforce these standards by providing templates, checklists, and automated controls.
Standardizing business processes offers several proven benefits:
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Provides a clear blueprint for tasks, reducing ambiguity and guesswork. | |
Improve the Customer Experience | Consistent processes lead to improved product quality and customer satisfaction. |
Create a Culture of Continuous Improvement | Establishes standard processes that foster collaboration and problem-solving across departments. |
Faster and Cheaper Implementation | Saves time and costs associated with expert consultations by standardizing before implementation. |
Teams that use process standardization achieve:
Consistency and quality control. Best practices ensure predictable and high-quality outcomes.
Improved efficiency and productivity. Streamlined steps reduce wasted time and resources.
Enhanced training and onboarding. New employees learn faster with clear instructions.
Easier process analysis and improvement. Standard operating procedures (SOPs) make it simple to monitor and enhance workflows.
For example, Eyuboglu Schools standardized their processes to support rapid growth. Their teams worked together to document procedures and use digital systems for tracking. As a result, they scaled operations smoothly and maintained high quality.
Note: Review and update standard processes regularly. Involve teams from different departments to keep standards relevant and practical.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement ensures that business process management never stands still. Teams and systems work together to review performance, gather feedback, and make changes. This approach helps organizations adapt to new challenges and stay competitive.
Several effective continuous improvement methodologies support efficient business process outcomes:
Lean Six Sigma focuses on reducing waste and improving quality.
Agile emphasizes flexibility and customer feedback.
Business Process Reengineering involves radical redesign for dramatic improvements.
Total Quality Management aims for long-term success through customer satisfaction.
Kaizen encourages small, ongoing changes that add up over time.
These methods help organizations:
Enhance efficiency and productivity.
Reduce waste and operational costs.
Drive sustainable growth and customer satisfaction.
Ensure improvements are intentional and data-driven.
Align with strategic objectives.
For instance, Harvest Operations Corp. used continuous improvement to reduce processing time by 90%. Their teams analyzed workflows, identified bottlenecks, and applied Lean principles. Systems tracked progress and provided real-time data, making it easier to measure success.
Tip: Encourage everyone to suggest improvements. Use data from systems to guide decisions and celebrate small wins along the way.
Continuous improvement turns process optimization into a habit. Teams that review and refine their work regularly achieve better results and build a culture of excellence.
Measuring Success
Measuring the success of business process optimization helps organizations understand what works and where to improve. Teams use clear metrics and benchmarks to track progress and prove the value of their efforts. These measurements guide future decisions and support a culture of continuous improvement.
A variety of metrics help organizations evaluate their process optimization initiatives. The table below outlines the most common types:
Metric Type | Description |
|---|---|
Metrics like Cycle Time, Error Rates, and Resource Utilization help assess the efficiency of processes. | |
Financial Impact Metrics | Cost Savings and Revenue Generation metrics quantify the financial benefits of process improvements. |
Customer Satisfaction Metrics | Metrics such as Customer Feedback, Retention, and Support Metrics gauge customer satisfaction levels. |
Employee Engagement Metrics | Employee Satisfaction and Productivity metrics measure the impact of process improvements on staff. |
Compliance and Risk Metrics | Metrics for Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management help ensure adherence to standards and mitigate risks. |
Continuous Improvement Metrics | Metrics tracking the Process Improvement Pipeline and Sustainability assess ongoing improvement efforts. |
Organizations often rely on specific benchmarks to evaluate the effectiveness of their process changes. These benchmarks provide clear targets and make it easier to compare results over time. Common benchmarks include:
Cycle Time: Measures the time required to complete a process from start to finish. Shorter cycle times often indicate greater efficiency.
Cost per Transaction: Tracks the cost of completing a specific task, such as processing an order. Lower costs suggest better resource management.
Error Rates: Measures the frequency of errors within a process. Fewer errors mean higher quality and reliability.
Customer Satisfaction: Assesses customer feedback through surveys and reviews. Higher satisfaction scores reflect improved service.
Resource Utilization: Tracks how effectively labor, materials, and technology are used. Better utilization leads to reduced waste and higher productivity.
Tip: Teams should select metrics that align with their business goals. Regularly reviewing these metrics helps organizations spot trends, address issues quickly, and celebrate improvements.
Best practices for measuring success include setting clear targets, using both quantitative and qualitative data, and sharing results with all stakeholders. Teams can use dashboards or scorecards to visualize progress and keep everyone informed. When organizations measure success consistently, they build trust and drive ongoing improvement.
Real-World Practices
Case Example
Many organizations have achieved measurable improvements by mapping and optimizing their business processes. The following table highlights how well-known companies applied these strategies:
Company | Example of Optimization |
|---|---|
Amazon | Implemented Kiva robots to enhance warehouse efficiency by reducing time spent walking, especially during peak seasons. |
Southwest Airlines | Streamlined workflows and used a single aircraft type to minimize turnaround time, achieving an average of 49 minutes. |
Kraft | Focused on process documentation and automation during the relocation of a production facility to improve efficiency. |
Uber | Utilized data-driven approaches to optimize trip fulfillment processes, enhancing service delivery and operational efficiency. |
Amazon transformed its warehouse operations by investing in robotics. Workers spent less time walking, which increased speed and accuracy. Southwest Airlines improved aircraft turnaround by using a single model and coordinating ground staff. Kraft documented every step during a facility move, then automated tasks to boost efficiency. Uber used analytics to refine trip fulfillment, which led to better customer experience and faster service.
Lessons Learned
Organizations have discovered several important lessons during process optimization projects:
Inadequate frontline engagement often leads to impractical solutions and resistance.
Overreliance on technology without fixing underlying process issues can waste resources.
Not setting clear objectives causes scattered efforts and project abandonment.
Insufficient resources slow down progress and reduce effectiveness.
Poor change management can derail even well-planned projects.
Many teams learned that a thorough analysis of resource requirements and skills is essential. Projects with unclear goals or missing baseline analysis often fail. About 60-70% of process optimization projects do not succeed, usually because teams did not define objectives or understand the current situation.
Tips for Success
Experts recommend several actionable steps for successful business process optimization:
Evaluate current processes to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
Map workflows using visual aids like flowcharts to clarify task sequences.
Set specific performance metrics (KPIs) to measure success.
Automate repetitive tasks to enhance efficiency and reduce errors.
Engage the entire business to foster a culture of process optimization.
Teams should keep process maps simple and clear. They need to define the purpose before starting and involve those who perform the work daily. Regular updates help keep maps relevant. Ownership and support from all levels ensure changes become part of daily routines. When teams focus on customer service processes, they see improvements in customer experience and overall performance.
Tip: Draw process maps and set clear goals for each process. Review and update regularly to maintain progress.
Mapping and optimizing business processes delivers lasting gains in quality, efficiency, and employee engagement. Teams that revisit and improve workflows see better customer satisfaction, faster response times, and higher morale. Leaders should analyze inefficiencies, redesign processes, and monitor key performance indicators for ongoing success. For deeper insights, explore guides on business improvement strategy, process training, and automation tools. Adaptive leadership and clear vision inspire teams to act. Those seeking to optimize with systems and teams can reach out for further information.
FAQ
What is the main goal of business process mapping?
Business process mapping helps teams see how work flows. It shows each step clearly. Teams use maps to find problems, remove waste, and improve results.
How often should organizations review their business processes?
Experts recommend reviewing processes at least once a year. Teams should also review after major changes, such as new technology or business growth.
Which tools work best for process mapping?
Popular tools include Lucidchart, Microsoft Visio, and Miro. These tools offer templates, easy editing, and team collaboration features.
Can small businesses benefit from process optimization?
Yes. Small businesses often see quick wins. They can save time, reduce errors, and improve customer service by mapping and optimizing their processes.
What are common mistakes in process optimization?
Teams often skip clear goal setting or forget to involve key staff. Some rely too much on technology without fixing basic process issues.
How does automation improve business processes?
Automation handles repetitive tasks. This reduces errors and saves time. Employees can focus on more important work.
What is the difference between process mapping and process documentation?
Process mapping uses diagrams to show steps visually. Process documentation describes each step in writing. Both help teams understand and improve workflows.
How can teams measure the success of process improvements?
Teams track metrics like cycle time, error rates, and customer satisfaction. Regular reviews help teams see progress and spot new improvement areas.



