Simple Steps to Enhance Your Business Processes

Enhancing business processes starts with adopting a clear methodology. Every organization, regardless of size, can achieve optimization of business processes by mapping workflows and using systems that support improvement. Companies report real gains: 21% save 10% or more, and 81% of enterprise organizations see over 15% internal rate of return.
Statistic | Percentage |
|---|---|
Companies saving 10% or more | 21% |
Enterprise organizations with >15% internal rate of return | 81% |
Business executives believing BPM helps achieve goals | 70% |
The most common benefits include improved efficiency, reduced costs, and better quality. Project managers save time, and resources increase in value. The chart below shows how organizations experience faster deployment and higher customer satisfaction.
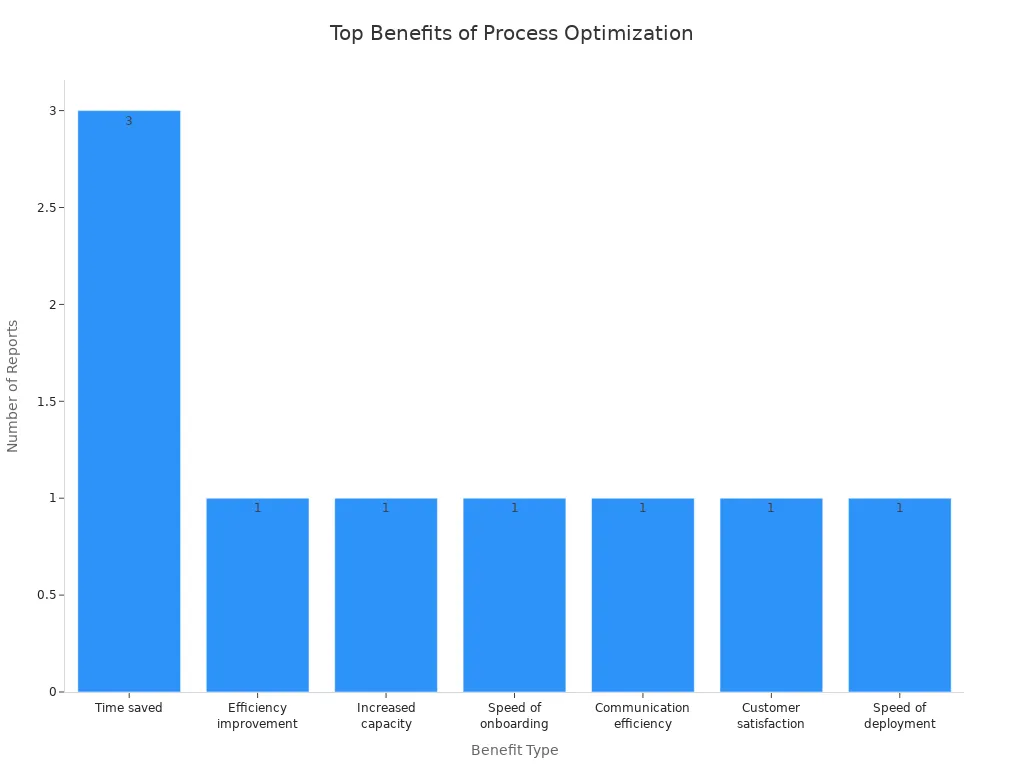
Following a step-by-step approach helps teams unlock these advantages quickly.
Key Takeaways
Adopt a clear methodology to enhance business processes and achieve optimization.
Mapping workflows helps identify inefficiencies and streamline operations.
Implementing optimized workflows can lead to a 25-30% reduction in operational costs.
Involve frontline workers in process changes to boost quality and innovation.
Use structured methods like Lean and Six Sigma to improve processes effectively.
Leverage technology and automation to reduce manual tasks and errors.
Set SMART goals to ensure clarity and focus in process improvement efforts.
Regularly review processes to maintain efficiency and adapt to changes.
Why Optimize?
Efficiency Gains
Companies pursue optimization of business processes to achieve faster and more reliable results. Studies show that organizations can reduce task completion time by 40% to 60% when they streamline their workflows. This improvement means employees spend less time on repetitive tasks and more time on valuable work. When teams align their processes with strategic goals, they add value to the business and enhance customer satisfaction.
Organizations typically see a 25-30% reduction in operational costs after implementing optimized workflows.
A well-optimized process helps teams work smarter, not harder. Employees can focus on solving problems and delivering quality service. As a result, businesses experience higher productivity and better outcomes.
Key reasons for process optimization include:
Reduces costs
Improves quality
Increases customer satisfaction
Cost Reduction
Reducing costs remains a top priority for many organizations. By identifying waste and streamlining operations, companies can save money and use resources more effectively. The following table highlights areas where businesses often find cost-saving opportunities:
Area of Optimization | Evidence |
|---|---|
Utility Expenses | Utility expenses contribute about 40% of overall business expenses, with strategic measures leading to direct cost savings. |
Technology Infrastructure | Optimizing technology infrastructure can reduce maintenance costs and improve performance, avoiding missed growth opportunities. |
Inventory Management | Excess inventory can drain resources, impacting storage costs and product obsolescence, indicating significant cost-saving potential. |
Customer Service | Analyzing the cost per support ticket helps identify inefficiencies in customer service processes, leading to potential cost reductions. |
A robust strategy is essential for reducing operational costs. Companies analyze current expenses and prioritize areas for improvement. Continuous fine-tuning of strategies ensures efficiency and agility in adapting to market changes.
Quality Improvement
Quality improvement stands as a major benefit of process optimization. Organizations that adopt lean methodologies identify and eliminate wasteful practices, which leads to better service delivery and increased productivity. Involving frontline workers in the optimization process allows companies to leverage their insights and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Lean transformation in service industries enhances service delivery and overall productivity.
Employee engagement in process changes boosts quality and innovation.
Data-driven decision-making ensures improvements align with customer needs and expectations.
When businesses focus on quality, they build trust with customers and create lasting value. Optimization of business processes supports consistent product quality and faster service delivery, which increases customer satisfaction and competitiveness.
Optimization of Business Processes
Structured Methods
Optimization of Business Processes begins with a systematic approach. Teams map workflows, analyze steps, and seek continuous improvement. Experts recommend several structured methods that help organizations achieve better results. The table below shows popular methodologies and their key focus areas:
Methodology | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|
Business Process Management | Systematic management and improvement of processes |
Lean Methodologies | Waste elimination and value maximization |
Six Sigma | Data-driven reduction of process variability |
Agile Practices | Iterative improvements and adaptability |
Teams use these methods to identify gaps and set clear goals. Systems and teams at leading companies have adopted Lean and Six Sigma to reduce errors and improve quality. Business Process Management helps organizations manage change and measure progress. Agile practices allow teams to adapt quickly and deliver value in short cycles.
Many organizations also use new approaches to stay competitive. These include:
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Hyper Automation
Real-time Data Analytics
Remote and Hybrid Work Adaptations
Sustainability-Driven Optimization
These strategies help systems and teams respond to market changes and customer needs.
Technology and Automation
Technology plays a major role in the Optimization of Business Processes. Automation and artificial intelligence (AI) eliminate manual tasks and reduce errors. Companies use AI to analyze data, make decisions, and improve accuracy. The following list highlights how different industries benefit from automation and AI:
Customer Service Automation: Companies like Telefonica use AI to answer routine questions, which leads to faster responses and higher customer satisfaction.
Finance and Accounting: KPMG uses AI for financial audits, increasing accuracy and saving time.
Supply Chain and Logistics: DHL employs AI for route planning and demand forecasting, which improves efficiency and lowers costs.
HR and Recruitment: Unilever uses AI tools to make hiring faster and more effective.
Marketing and Sales: Coca-Cola personalizes marketing campaigns with AI, boosting customer engagement.
Healthcare: AI helps forecast patient outcomes and streamlines care delivery.
Automation delivers several advantages:
Improved decision-making with data-driven insights
Increased agility as processes adapt without manual changes
Scalability across departments without extra overhead
Consistent outcomes with fewer errors
Resource optimization, allowing people to focus on strategic work
Systems and teams at client organizations have seen measurable results. For example, German Engineering GCC digitized core business processes and reduced Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) costs by 25%. US Healthcare GCC redesigned its operating model and cut quality-related costs by 30%. Canadian Insurance GCC automated workflows and reduced capacity needs by 35% over two years.
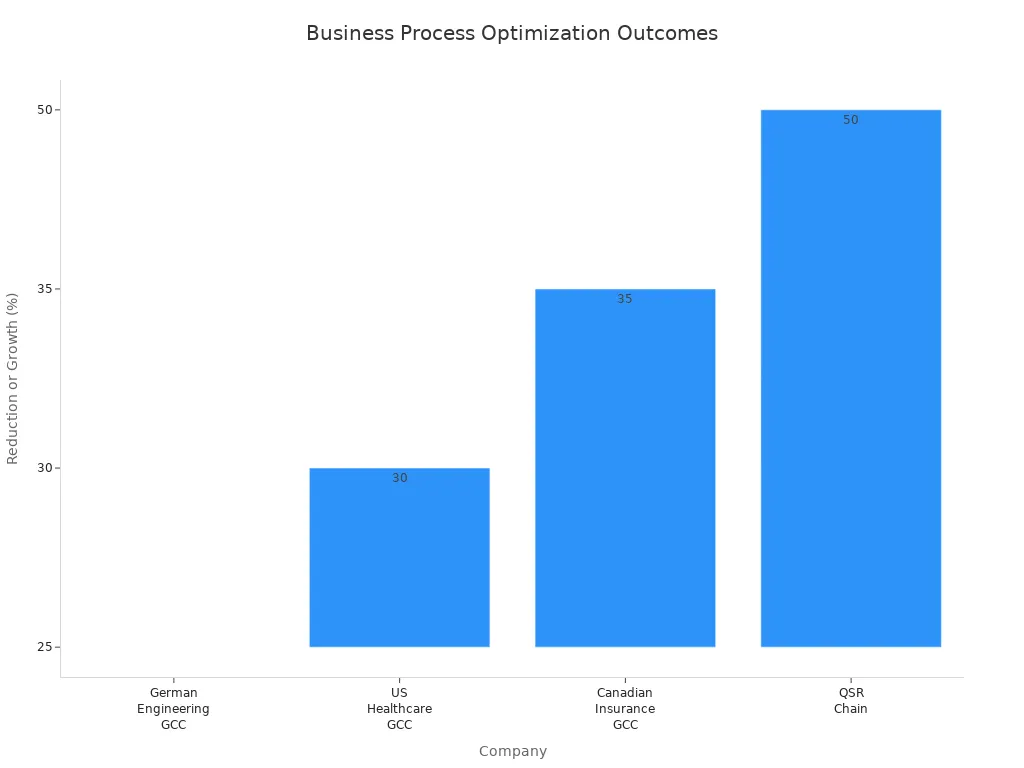
Other companies have achieved similar success:
Company | Strategy | Measurable Outcome |
|---|---|---|
Kraft | Migrated production facility with process documentation | More efficient move into Canadian plant |
Uber | Data-driven fulfillment optimization | Enhanced trip efficiency and customer service |
Accenture | Redesigned finance, procurement, and HR processes | Improved service delivery for taxpayers |
These examples show how systems and teams use technology to drive process optimization and deliver real business value.
Standardization
Standardization supports the Optimization of Business Processes by creating consistent procedures. Organizations establish clear steps for each task, which improves efficiency and reduces variability. Teams follow standard processes to save costs and deliver higher quality.
Standardization creates reliable operations and helps companies respond quickly to market demands.
It ensures compliance with laws and regulations, lowering the risk of penalties.
Employees make fewer mistakes and experience less confusion, which allows them to focus on their work.
Systems and teams at client organizations have used standardization to streamline operations and maintain quality. For example, process standardization helped a quick-service restaurant chain redesign its outlet placement strategy, resulting in a 50% increase in brand visibility and revenue growth.
Teams that use structured methods, technology, and standardization achieve lasting improvements. Readers who want to learn more about how systems and teams can optimize business processes are invited to reach out for further information.
Map Processes

Workflow Visualization
Organizations use workflow visualization to gain a clear picture of how tasks move through each stage. Visual tools, such as flowcharts or diagrams, help teams see every step in a process. The human brain interprets images much faster than text, which makes visual workflows especially effective. People can spot delays, bottlenecks, or duplicated efforts quickly. Project managers observe how resources are allocated and used across different tasks.
Visualizing workflows increases transparency and promotes accountability. Teams understand who is responsible for each step and can track progress with ease.
Workflow visualization offers several advantages:
Teams identify bottlenecks early and address them before they become major issues.
Planning becomes simpler, and team members exchange information more efficiently.
Visual workflows make it easier to explain work processes and assign responsibilities.
Organizations focus on value-added activities, which leads to increased productivity and reduced wasted time.
A well-designed workflow map highlights steps that could be automated or eliminated. Teams evaluate how each step aligns with strategic goals. They prioritize improvements that deliver the greatest impact. Before making changes, teams assess risks and dependencies to avoid unexpected problems.
Best practices for mapping business processes include:
Highlight steps for automation or elimination.
Evaluate alignment with strategic goals.
Prioritize high-impact improvements.
Design the improved 'to-be' process.
Assess risks or dependencies before implementation.
Defining key performance indicators (KPIs) helps teams track progress. Setting a review frequency, such as quarterly or annually, ensures ongoing improvement. Assigning a process owner keeps updates on track, while a feedback loop encourages future enhancements.
Stakeholder Involvement
Stakeholder involvement plays a vital role in successful process mapping. Teams create stakeholder maps to visualize relationships and roles. This approach improves communication and ensures everyone understands their responsibilities.
Benefit of Stakeholder Mapping | Description |
|---|---|
Identifies key partners | Teams recognize who influences the process most. |
Understands influence | Stakeholder maps show how each person or group affects outcomes. |
Develops management strategy | Teams plan how to engage and manage stakeholders effectively. |
Creating a stakeholder map helps teams develop a communication and engagement plan. This plan addresses the needs of all parties and manages expectations. When stakeholders participate in mapping, they share valuable insights and help identify improvement opportunities.
Involving stakeholders leads to better alignment of roles and smoother implementation of changes.
Teams define KPIs and assign process owners to maintain accountability. Establishing a feedback loop allows stakeholders to suggest improvements and keeps the process dynamic. Regular reviews ensure that the process continues to meet organizational goals.
By combining workflow visualization and stakeholder involvement, organizations build a strong foundation for process optimization. Teams work together to create efficient, transparent, and adaptable processes that drive business success.
Analyze Data
Key Metrics
Successful organizations rely on data to measure and improve their business processes. Teams select key metrics that reflect the health and performance of each workflow. These metrics help managers understand where processes excel and where they need attention.
Data-driven decisions lead to better outcomes and more efficient operations.
The most commonly used metrics include:
Efficiency: Teams calculate the ratio of output to input. High efficiency means resources are used wisely.
Effectiveness: Managers check if processes meet their goals. Effectiveness shows whether the intended results are achieved.
Cycle Time: Leaders measure the total time from start to finish. Shorter cycle times often signal a well-optimized process.
Process Yield: Teams look at the number of correct outputs compared to total outputs. A high yield points to fewer errors and better quality.
Metric | What It Shows | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
Efficiency | Resource utilization | Reduces waste and saves money |
Effectiveness | Goal achievement | Ensures desired outcomes |
Cycle Time | Speed of process completion | Improves customer experience |
Process Yield | Quality of outputs | Boosts reliability |
Managers use these metrics to set benchmarks and track progress. They compare results across departments and time periods. This approach helps teams focus on areas that need improvement.
Trends
Analyzing trends in process data gives organizations a clear view of performance over time. Teams study patterns in key metrics to spot strengths and weaknesses. This method helps leaders make informed decisions and plan future improvements.
Trend analysis allows managers to evaluate employee and organizational performance.
Teams track key performance indicators (KPIs) over weeks, months, or years. This tracking highlights areas that need attention.
Leaders foster accountability by sharing results and encouraging teams to improve.
? Trend analysis supports a culture of continuous improvement.
Organizations use historical data to understand how processes change. They identify best practices and learn from past successes. Benchmarking against competitors helps companies stay ahead in the market.
Teams use trend data to pinpoint opportunities for improvement.
Managers compare their results with industry standards.
Leaders adjust strategies based on what the data reveals.
By combining key metrics and trend analysis, organizations build a strong foundation for process optimization. Teams make smarter decisions, improve performance, and achieve lasting success.
Find Bottlenecks
Identify Issues
Bottlenecks slow down business processes and reduce efficiency. Teams need to spot these trouble spots early to keep workflows running smoothly. Several proven methods help organizations identify where problems occur.
Visualization Techniques: Teams use flowcharts, Kanban boards, or business process management (BPM) tools to map out each step. Value-stream mapping helps track how work moves through the process.
Data Analysis: Managers analyze performance data by tracking key metrics like cycle time, throughput, and work-in-progress (WIP) levels. These numbers reveal where delays happen most often.
Employee Input: Frontline employees often see issues before anyone else. Surveys, interviews, and daily stand-ups give them a chance to share insights about workflow pain points.
Workflow Diagnosis: Teams conduct workflow audits and use fishbone diagrams to find the root causes of slowdowns.
Real-time Monitoring: Monitoring tools track cycle times and workflow inefficiencies as they happen, allowing teams to react quickly.
Simulations: 'What-if' simulations test different scenarios to see how changes might affect workflow efficiency.
Teams that combine these methods gain a clear picture of where bottlenecks form and how they impact the business.
Prioritize
After identifying bottlenecks, teams must decide which issues to tackle first. Not every problem needs immediate attention. Prioritization ensures that resources focus on changes with the greatest impact.
The table below shows key criteria teams use to rank process issues:
Criteria Type | Questions |
|---|---|
Qualitative | 1. Can the process be improved within 30 days without significant financial investment? |
2. Does improving this process align with your organization’s core values and mission? | |
Quantitative | 1. Can the process improvement be achieved with existing staff within a reasonable timeframe? |
2. How will improving this process affect customer satisfaction? | |
3. Will improving this process directly increase revenue? | |
4. Will this process improvement positively impact EBITDA? |
Teams answer these questions to weigh the benefits and feasibility of each improvement. Quick wins—changes that require little time or money—often move to the top of the list. Projects that align with company values or boost customer satisfaction also receive higher priority.
By focusing on the most important bottlenecks first, organizations see faster results and build momentum for future improvements.
Teams that use a structured approach to identify and prioritize bottlenecks create a solid foundation for lasting business process optimization.
Set Goals
Clear Objectives
Setting clear objectives forms the backbone of any successful process improvement effort. Teams need goals that everyone can understand and measure. Vague or broad targets often lead to confusion and wasted effort. Instead, organizations benefit from using the SMART framework to guide their goal-setting process.
The SMART approach helps teams create objectives that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Each component ensures that goals are clear and actionable. The table below outlines the SMART criteria:
SMART Component | Description |
|---|---|
Specific | Objectives should be precise and clear to all stakeholders. Use plain language and action verbs. |
Measurable | Define how progress will be tracked with specific measures and targets. Include data sources. |
Achievable | Ensure objectives are realistic given available resources and time. |
Relevant | Align objectives with broader goals and the organization's mission. |
Time-bound | Set a reasonable deadline for achieving the objectives. |
Teams that use SMART goals can track progress more easily. For example, a team might set a goal to reduce order processing time by 20% within six months. This goal is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. Everyone knows what success looks like and how to measure it.
? Clear objectives give teams a sense of direction and purpose. They help everyone stay focused on what matters most.
Team Alignment
Team alignment ensures that everyone works toward the same objectives. When teams align their efforts, they avoid confusion and reduce wasted time. Alignment starts with clear communication and shared understanding.
To achieve strong team alignment during the goal-setting phase, organizations can follow these steps:
Define your goals clearly: Clearly defined goals are essential for team alignment. Vague goals lead to confusion.
Communicate your goals from the top-down: Consistent communication ensures everyone understands the goals and their roles.
Break down your goals: Decomposing larger goals into smaller, actionable steps helps team members see how they contribute to the overall objectives.
Teams that follow these steps often see several benefits:
Improved productivity: Reduces confusion and conflicts.
Enhanced communication: Fosters better collaboration and idea generation.
Higher employee engagement: Employees feel more motivated when they understand their role in the larger picture.
When everyone understands the goals and their part in achieving them, teams work more efficiently. Leaders should encourage open discussions and answer questions about objectives. This approach builds trust and helps teams move forward together.
Note: Regular check-ins help teams stay aligned and adjust goals as needed. Alignment is not a one-time event but an ongoing process that supports continuous improvement.
Implement Changes
Quick Wins
Teams often look for quick wins when improving business processes. Quick wins deliver fast results and build momentum for larger changes. They require minimal resources and can be implemented without complex planning. Many organizations start with small adjustments that make a noticeable difference.
The table below shows examples of quick wins that teams can use to improve business processes:
Quick Win | Description |
|---|---|
Automate One Repetitive Task | Save time by automating tasks like scheduling posts or sending invoices. |
Delegate One Responsibility | Let go of a time-consuming task by delegating it to a team member or outsourcing. |
Increase Your Visibility | Get in front of more potential clients through networking, ads, or guest posting. |
Teams also benefit from simple changes such as:
Minor procedure change
Communication improvement
Part substitution
Training on best practices
Error proofing a process step
Minor layout change
Simple visual management
Many organizations eliminate internal emails by using tools like Slack or Flock. They enhance communication by emphasizing its importance within the team. These actions help teams work faster and reduce confusion.
Quick wins create positive energy and encourage teams to continue improving. Small changes often lead to bigger successes.
Managers should identify areas where quick wins are possible. They can ask team members for suggestions and review current workflows. Teams that focus on quick wins see immediate benefits and set the stage for long-term improvements.
Assign Roles
Assigning roles and responsibilities ensures that process changes succeed. Clear roles help teams avoid confusion and keep projects on track. Leaders must include everyone who will have assigned responsibilities.
A step-by-step approach helps teams assign roles effectively:
Determine participants. Include all team members who will have responsibilities.
Prepare your platform. Create a shared space, either online or physical.
Schedule the session. Plan for 2–3 hours, with a shorter follow-up 1–4 weeks later for review and adjustments.
List all team responsibilities. Document all current responsibilities within the team.
List all team roles. List all existing roles and planned near-future additions.
Use visual role representation. Assign unique icons or stickers to each role for quick identification.
Assign initial responsibilities. Tag each responsibility with the role believed to be responsible.
Gather responsibilities with consensus. Group responsibilities where all team members agree on the assigned role.
Build alignment around remaining responsibilities. Address all responsibilities with mixed role assignments to reach consensus.
Assign roles to people responsible for them. Ensure clarity on who will manage each role and associated responsibilities.
Clear role assignment increases accountability and helps teams work together smoothly.
Teams should revisit roles and responsibilities regularly. Leaders encourage feedback and make adjustments as needed. When everyone knows their role, process changes happen more efficiently and with less resistance.
Monitor Results
Track KPIs
Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) helps organizations measure the impact of process changes. KPIs provide clear data that shows whether a new process delivers the expected results. Teams select KPIs that match their goals and reflect the outcomes they want to achieve.
The table below highlights some of the most effective KPIs for monitoring business process improvements:
KPI Type | Description |
|---|---|
Customer Feedback Scores | Measures customer satisfaction and can indicate the success of process changes. |
Net Promoter Score (NPS) | Assesses customer loyalty and the likelihood of recommending the service, reflecting process impact. |
Customer Retention Rates | Indicates how well the organization retains customers after changes, a direct measure of success. |
Change Success Rate | Broad measure of whether the project achieved its intended objectives. |
Benefit Realization | Assesses productivity or efficiency improvements resulting from the change initiative. |
Stakeholder Satisfaction | Transforms feedback into quantifiable metrics to gauge perception of the change effectiveness. |
KPIs should always reflect the specific outcomes the team wants to achieve. They help measure the success of each change and keep everyone focused on results.
Teams follow a simple process to use KPIs effectively:
Benchmark the existing situation before starting the project.
Set measurable and achievable targets for each KPI.
Use KPIs to track improvement and maintain enthusiasm for the change project.
Benchmarking helps teams understand where they started. Setting targets gives everyone a clear goal. Tracking progress against KPIs shows if the changes work and builds support for future improvements.
Review
Regular reviews ensure that process changes deliver lasting benefits. Teams use structured methods to evaluate the success of each improvement. Reviewing results helps organizations spot new opportunities and prevent old problems from returning.
Common review methods include:
Understanding current processes by mapping them out to find inefficiencies and bottlenecks.
Using flowcharts and diagrams to visualize the current state and highlight areas for improvement.
Applying value stream mapping and fishbone diagrams to pinpoint the root causes of slowdowns or errors.
A popular approach for reviewing process changes follows these steps:
Define the problem clearly.
Measure performance by collecting data.
Analyze the data to find root causes.
Improve the process by implementing solutions.
Control the new process to sustain gains.
Six Sigma, a data-driven methodology, supports this approach. It helps teams identify and reduce errors, leading to more efficient operations.
Regular reviews keep teams focused on continuous improvement. They help organizations adapt to changes and maintain high performance.
By tracking KPIs and conducting structured reviews, organizations ensure that process improvements last and continue to deliver value.
Engage Employees
Training
Effective training prepares employees to adopt new business processes with confidence. Organizations achieve better results when they tailor training programs to meet the needs of their teams. User-centric training design focuses on the specific skills and preferences of employees. Support systems provide ongoing resources, helping staff adjust to new workflows.
Training Method | Description |
|---|---|
User-Centric Training Design | Tailoring training programs to meet the specific needs and preferences of employees. |
Support Systems | Providing ongoing assistance and resources to help employees adapt to new processes. |
Recognition Programs | Implementing incentives to encourage and reward employees for adopting new business processes. |
Data-Driven Strategies | Utilizing analytics to assess training effectiveness and make necessary adjustments. |
Project-based learning introduces real-world challenges. Employees solve problems they may encounter in their roles, which strengthens their ability to adapt. This approach builds problem-solving skills and prepares teams for future changes.
Organizations streamline their technology stack to improve collaboration and data visibility. They conduct research to identify employee needs and preferences. Dedicated time for training helps staff balance learning with daily duties.
Training works best when employees feel supported and recognized for their efforts. Incentives and ongoing assistance encourage staff to embrace new processes.
Feedback
Feedback drives continuous improvement in business processes. Organizations encourage a growth mindset by showing that feedback leads to learning and progress. They use models like the SBI (Situation-Behavior-Impact) Model to structure feedback with clarity and specificity.
Encourage a growth mindset. Feedback becomes a tool for learning.
Use structured models for clarity. The SBI Model helps teams understand the impact of their actions.
Invite two-way dialogue. Employees share perspectives and suggest solutions.
Schedule regular check-ins. Consistent feedback builds transparency.
Regular feedback loops foster communication within teams. They build trust between employees and management. These loops help organizations identify areas for improvement and reinforce strengths.
Teams that share feedback openly create a transparent environment. Employees feel respected and valued, which boosts engagement and motivation.
Productivity increases when workers feel empowered to take initiative.
Engagement rises in a culture of continuous feedback.
Employee satisfaction grows when staff know their opinions matter.
Organizations schedule regular feedback meetings and foster trust. They treat feedback as a tool for growth, not criticism. This approach supports continuous improvement and helps teams adapt to new business processes.
Continuous Improvement
Ongoing Review
Continuous improvement relies on regular and structured reviews of business processes. Organizations that commit to ongoing review see lasting benefits. They use best practices to ensure each review delivers value and supports long-term goals.
Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
Regular assessments | Teams conduct reviews at least once a year to keep processes effective. |
Experienced team | A knowledgeable team leads the review for accurate results. |
Comprehensive template | Teams use detailed templates to maintain consistency in every review. |
Goal identification | Clear goals and scope guide the review process from the start. |
Systematic optimization | Teams plan each step and expected outcome for process improvement. |
Suitable metrics | Metrics help measure the impact of changes and track progress. |
Time allocation | Teams set aside dedicated time to complete reviews thoroughly. |
Reporting outcomes | Results are documented and shared for transparency and learning. |
A facilitator who understands the organization’s operations leads the review. Team members receive regular training to stay updated on new processes and technology. This approach helps teams identify gaps, measure results, and plan improvements.
Ongoing reviews bring several long-term benefits. Organizations that review processes regularly experience enhanced efficiency and productivity. Employees feel more engaged because they contribute to improvements. Teams become more adaptable to changes in the market or technology. Quality improves as teams identify and fix defects. Cost savings increase as wasteful practices are eliminated. A culture of review also encourages innovation and creativity, leading to better customer satisfaction.
Recognize Success
Recognizing and rewarding success motivates teams to continue improving. Organizations use a variety of strategies to celebrate achievements and reinforce positive behaviors.
Strategy Type | Description |
|---|---|
Employee of the Month | Highlights individual achievements and encourages friendly competition. |
Objective Metrics Recognition | Publicly acknowledges those who meet clear, measurable improvement goals. |
Non-Cash Rewards | Offers alternatives like gift certificates or experiences to reward contributions. |
Consistent Recognition Programs | Maintains a structured approach to sustain a culture of improvement. |
Simple Acknowledgment | Uses verbal praise and appreciation to recognize daily efforts. |
Peer Recognition Programs | Encourages employees to recognize each other’s contributions. |
Professional Growth Opportunities | Provides resources and training for employee development. |
Special Events | Hosts gatherings to celebrate team achievements and boost morale. |
Many organizations use points-based programs, nomination systems, and special events to celebrate both individual and team accomplishments. Simple acknowledgments, such as a thank you or public praise, can have a big impact on morale. Peer recognition programs foster a sense of community and shared purpose. Professional growth opportunities show employees that the organization values their development.
A strong recognition program helps build a culture where continuous improvement thrives. Employees feel valued and motivated to contribute new ideas. Teams that celebrate success together are more likely to sustain high performance and adapt to future challenges.
Optimizing business processes brings efficiency, cost savings, and higher quality. Experts recommend these steps for success:
Identify processes that need improvement
Map out current workflows
Analyze and prioritize changes
Redesign and test new processes
Implement improvements
Set clear business goals
Target tasks for automation
Monitor and review progress
Starting with one step helps teams build momentum. Continuous improvement leads to long-term growth and lasting results.
FAQ
What is a business process?
A business process is a set of steps that a company follows to complete a task or deliver a service. These steps help teams work together and achieve business goals.
Why should a company optimize its business processes?
Optimization helps companies save time, reduce costs, and improve quality. Teams can work more efficiently and deliver better results to customers.
How can technology improve business processes?
Technology automates repetitive tasks and reduces errors. Teams use software to track progress, analyze data, and make better decisions.
What is process mapping?
Process mapping creates a visual diagram of each step in a workflow. Teams use these diagrams to find bottlenecks and improve efficiency.
How often should a company review its processes?
Companies should review processes at least once a year. Regular reviews help teams spot problems early and keep workflows efficient.
Who should be involved in process improvement?
Teams should include employees from different departments. Involving people with different skills and knowledge leads to better solutions.
What are quick wins in process improvement?
Quick wins are small changes that deliver fast results. Teams can automate a simple task or improve communication to see immediate benefits.
How does feedback help with process optimization?
Feedback helps teams learn what works and what needs improvement. Regular feedback encourages employees to share ideas and support continuous improvement.



