Simple Ways to Organize Small Business Systems for Growth
Organizing small business systems starts with choosing a clear methodology and using resources that support growth. Owners who systemize daily tasks save time and reduce errors. Automation and delegation help businesses recover 8 to 15 hours per week, and response speed improves by 25%. Systems like templates and software allow teams to focus on strategic work instead of routine chores.
Key Takeaways
Organizing small business systems saves time and reduces errors, allowing owners to focus on growth.
Implementing automation can recover 8 to 15 hours per week, improving response speed by 25%.
Clear procedures and documented workflows minimize mistakes and enhance team efficiency.
Regular system checks help maintain efficiency and prevent problems before they escalate.
Using templates and checklists standardizes tasks, ensuring consistency and quality across the team.
Effective communication systems build trust and improve client relationships through timely responses.
Choosing the right tools, like project management apps and accounting software, supports organization and growth.
Involving the team in system reviews fosters a culture of improvement and enhances overall morale.
Why Small Business Systems Matter
Growth & Efficiency
Small Business Systems play a vital role in helping companies grow and operate efficiently. Organized systems allow owners to analyze their strengths and weaknesses. This self-analysis helps them find market opportunities that larger competitors might miss. Businesses that focus on excellence in every area, from product quality to customer service, gain a strong advantage. Effective marketing and public relations also become easier with clear systems in place.
A well-structured business can measure and improve its performance. The table below shows how organized systems impact important efficiency metrics:
Metric | Impact on Efficiency |
|---|---|
Average Order Processing Time | Faster order fulfillment increases productivity. |
Order Accuracy | Correct orders boost customer satisfaction. |
Customer Satisfaction | Loyal customers return and refer others. |
Cost Reduction | Less waste means more savings. |
Employee Training Hours | Better training leads to higher productivity. |
When companies use Small Business Systems, they see improvements in revenue growth, cost reduction, and overall efficiency. These systems help maintain high quality and keep customers satisfied.
Error Reduction
Mistakes can cost small businesses time and money. Systematization acts as a safeguard against errors and inconsistencies. When companies clearly define procedures and standards, they lower the risk of mistakes during daily tasks. Documented workflows give employees a reliable reference, which reduces misunderstandings and keeps everyone on track.
Many businesses use software solutions and ERP systems to limit errors. These tools help prevent incorrect item references and other common mistakes. By following set processes, teams can deliver consistent results and avoid costly problems.
Systematization reduces errors and inconsistencies.
Clear procedures and standards minimize mistakes.
Documented workflows serve as a reference for staff.
Software and ERP systems help prevent common errors.
Stress Prevention
Running a small business can feel overwhelming. Systematizing tasks creates a more organized workflow, which helps reduce stress for owners and employees. A set schedule helps regulate energy and focus throughout the day. Prioritizing challenging tasks during peak energy times leads to better results.
Automation also plays a key role in stress prevention. By automating repetitive tasks, business owners save time and mental energy. This allows them to focus on important decisions and growth opportunities.
Organized workflows lower stress levels.
Schedules improve focus and energy management.
Automation saves time and reduces mental fatigue.
Tip: Owners who use Small Business Systems often find they have more time to plan for the future and less worry about daily operations.
Key Areas to Systemize
Marketing
Marketing stands as a core area for systemization in small businesses. Research shows that marketing systems, when organized, deliver measurable improvements in customer retention, repeat purchases, and sales. Companies often benefit from automating their marketing efforts and using data-driven strategies.
Social Media
Social media platforms allow businesses to reach new audiences and engage existing customers. Owners who schedule posts and use analytics tools can track engagement and adjust strategies quickly. Automated posting tools help maintain a consistent online presence. Teams often create content calendars to plan campaigns and avoid last-minute rushes.
Scheduling posts increases consistency.
Analytics tools help measure engagement.
Content calendars prevent missed opportunities.
Email Campaigns
Email campaigns remain one of the most effective marketing tools. Automated workflows and personalized messages drive higher open rates and sales. The table below highlights results from small businesses that systemized their email marketing:
Business Name | Metric | Result |
|---|---|---|
Boutique | Customer Retention Increase | 78% |
Boutique | Repeat Purchases Increase | 45% |
Boutique | Reduction in Manual Errors | 32% |
Boutique | Sales Increase | 25% |
Shapeways | Email Open Rate Increase | 238% |
Shapeways | Click-Through Rate Increase | 525% |
Thomson Reuters | Reduction in Lead-to-Conversion Time | 72% |
Thomson Reuters | Revenue Increase from Marketing Efforts | 175% |
Red Hot Marketing | Revenue Generated per 1,000 Emails Sent | $1,000 |
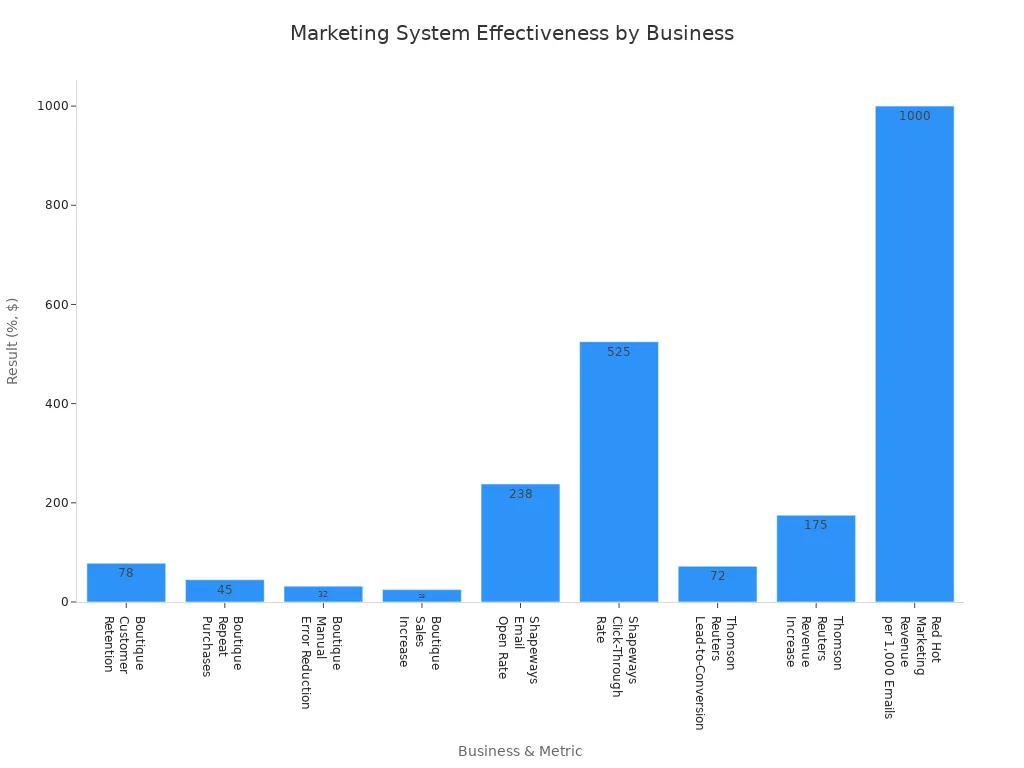
Personalized email campaigns and automated workflows led to a 78% increase in customer retention and a 45% rise in repeat purchases. Automation also reduced manual errors by 32% and boosted sales by 25%.
Client Communication
Systemizing client communication ensures that every customer receives timely and accurate responses. Businesses use templates and follow-up schedules to maintain professionalism and build trust.
Response Templates
Response templates save time and create consistency. Employees use pre-written replies for common questions, which reduces errors and speeds up communication. Templates also help new staff learn best practices quickly.
Follow-Ups
Follow-up systems remind teams to check in with clients after initial contact. Automated reminders and CRM tools track conversations and ensure no client gets overlooked. The table below outlines proven strategies for improving client communication:
Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
Active Listening | This technique involves fully concentrating, understanding, responding, and remembering what the client is saying, which builds trust and ensures accurate understanding of client needs. |
Persona-Based Communication | Adjusts communication style, content, and frequency to meet the specific needs and preferences of each client, enhancing message effectiveness and relationship building. |
Multi-Channel Communication | Utilizes various platforms (email, phone, chat, social media) to connect with clients on their preferred channels, making communication more convenient and effective. |
Measurement and Feedback Loops | Establishes a structured way to gather, analyze, and act on client feedback regarding communication effectiveness, ensuring ongoing improvement in client service. |
Operations
Operations form the backbone of every business. Systemizing operational processes increases efficiency and reduces mistakes.
Task Management
Task management systems help teams organize daily work. Owners assign tasks, set deadlines, and monitor progress using project management tools. These systems encourage accountability and make it easier to spot bottlenecks.
Inventory
Inventory management systems track stock levels and prevent shortages or overstocking. Automated alerts notify staff when supplies run low. Businesses often use software to record inventory movements and generate reports.
Industry research highlights several areas that benefit most from systematization:
Financial Systems
Marketing Systems
Human Resources Systems
Supply Chain Systems
Successful small businesses aim for continuous improvement by gathering employee feedback and optimizing operations. Choosing the right CRM tool and outsourcing non-core activities also supports growth.
Tip: Small Business Systems in these key areas help owners save time, reduce errors, and focus on growth.
Finance
Managing finances stands as a critical part of every small business. Owners who organize financial systems can improve accuracy, ensure compliance, and make better decisions. Two main areas to systemize include invoicing and expenses.
Invoicing
A reliable invoicing process helps businesses get paid on time and maintain healthy cash flow. Many owners use accounting software to automate invoice creation and tracking. These tools send reminders to clients and record payments automatically. Automation reduces manual errors and saves valuable time.
A hybrid finance solution combines technology with expert support. This approach allows small businesses to automate basic tasks while receiving strategic guidance from professionals. Some companies choose traditional accountants or in-house finance managers, depending on their size and needs.
Tip: Setting clear payment terms on every invoice helps prevent confusion and late payments.
The table below shows common invoicing system features and their benefits:
Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
Automated Reminders | Fewer late payments |
Digital Records | Easy tracking and reporting |
Custom Templates | Professional appearance |
Payment Integration | Faster transaction processing |
Implementing robust accounting software with built-in rules and standards ensures consistent compliance. Financial controls act as a safety net, reducing the risk of fraud and accounting errors.
Expenses
Tracking expenses helps owners understand where money goes and identify areas to save. Organized expense systems use technology to record purchases, categorize spending, and generate reports. Many businesses set up approval processes for larger expenses to maintain oversight.
Utilizing technology fills resource gaps and helps prevent errors in accounting data. Financial controls provide oversight, assisting owners in maintaining accurate financial reporting. Regular reviews of expense reports allow businesses to spot trends and adjust budgets as needed.
A simple expense management system often includes:
Digital receipt storage
Automated expense categorization
Monthly expense reports
Approval workflows for large purchases
Owners who use Small Business Systems in finance can make informed decisions and avoid costly mistakes. Accurate financial records support compliance and help businesses prepare for growth.
Note: Regularly updating financial systems keeps data accurate and ensures compliance with regulations.
Organizing Small Business Systems

Organizing business systems helps teams work smarter and achieve growth. Owners who follow a clear process can improve efficiency and reduce mistakes. This section explains how to map processes, use checklists and templates, and implement automation and delegation.
Process Mapping
Process mapping gives a clear view of how tasks move from start to finish. Owners use this method to spot problems and make improvements. The following steps outline how small organizations can map their processes:
Define objectives. Set clear goals, such as improving user experience or increasing retention.
Gather the team. Include people with different roles, such as product managers and customer support.
Outline steps. List each action, from first contact to final delivery.
Identify inputs and outputs. Note what goes into each step and what comes out.
Determine metrics. Choose ways to measure success, like engagement or satisfaction scores.
Create the map. Use flowcharts or templates to show each step visually.
Review and refine. Look for friction points and make changes to improve the process.
Implement and monitor. Put the new process into action and track results.
Owners also separate human tasks from system-based tasks. They establish the order of steps, look for redundancies, and use standard symbols in flowcharts. Sharing the process map with the team helps gather feedback and spot areas for improvement.
Tip: Regularly monitor mapped processes to find new ways to boost performance.
Checklists & Templates
Checklists and templates help teams complete tasks the same way every time. They reduce confusion and make training easier. The table below shows how these tools improve consistency in small business operations:
Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
SOP checklists act as blueprints for repeatable success. | Ensures no detail is overlooked, leading to uniform task completion. |
Step-by-step roadmap for routine tasks. | Reduces confusion and helps employees stay focused and confident. |
SOPs ensure workflow consistency across departments. | Guarantees high-quality outcomes regardless of who performs the task. |
Well-crafted SOP checklist serves as a training manual. | Minimizes onboarding time and reduces costly mistakes. |
Documented processes allow for tracing errors back to steps. | Facilitates root cause analysis and prevents future errors. |
Repeatable systems enable sustainable growth. | Allows for replication of successful processes across new teams or locations. |
Owners use checklists to guide daily work and templates to standardize documents. These tools help teams avoid missing steps and ensure high-quality results. Documented processes also make it easier to trace errors and fix problems quickly.
Note: Checklists and templates support growth by making successful systems easy to repeat.
Automation & Delegation
Automation and delegation free up time for important work. Owners identify tasks that technology can handle, such as sending follow-up emails or managing invoices. They also delegate tasks like content writing or digital marketing to skilled team members or contractors.
Best practices for automation and delegation include:
Identify repetitive and time-consuming tasks for automation.
Focus on areas where automation boosts productivity or revenue.
Audit daily and weekly tasks to decide which to automate or delegate.
Use technology for predictable tasks and assign creative work to people.
Popular automation tools include Mailchimp, HubSpot, Buffer, and Hootsuite for marketing. Customer service teams use Zendesk, Freshdesk, chatbots, and Calendly. Finance and operations benefit from QuickBooks, Xero, Stripe, and PayPal.
Owners assess their operations, automate lead generation and customer support, and delegate specialized tasks. This approach helps teams focus on strategic goals and reduces manual errors.
Tip: Combining automation and delegation with checklists and templates creates a strong foundation for Small Business Systems.
Practical Examples
Marketing Checklist
Small businesses often rely on marketing checklists to keep campaigns organized and effective. Systems and teams use these checklists to ensure every step receives attention. A well-structured checklist helps teams build strong brands, reach new customers, and maintain consistency.
Purpose | |
|---|---|
Post-Hailstorm Roof Inspection Guide | Helps roofers provide valuable service to clients |
Home Color Selection Checklist | Assists painters in guiding customers' choices |
Wedding Cake Planning Timeline | Aids bakers in organizing wedding cake orders |
Marketing teams at systems and teams follow a sequence of actions to maximize results:
Create a strong brand identity.
Build a website to improve online presence.
Prioritize great customer service.
Establish a social media presence.
Activate email marketing.
Invest in content marketing.
Try online advertising.
Each step supports growth and helps businesses connect with their target audience. Teams use these checklists to avoid missing important tasks and to measure progress over time.
Tip: Marketing checklists allow teams to track campaign performance and adjust strategies quickly.
Communication Template
Communication templates play a key role in streamlining client interactions. Systems and teams use these templates to save time and ensure every message includes important details. Email templates provide consistent communication, which enhances client support and builds trust.
Email templates streamline processes and prevent overlooked details.
They save time and provide consistent communication, enhancing client support and value.
A typical communication template includes:
Greeting and client name
Purpose of the message
Key information or updates
Next steps or actions required
Contact information for follow-up
A good client portal is more than just a communication tool; it serves as a centralized hub where clients can access project updates, share files, and provide feedback in real-time. This helps to reduce misunderstandings, streamline workflows, and improve overall productivity.
Teams at systems and teams use communication templates to respond quickly and maintain professionalism. Templates also help new staff learn best practices and deliver high-quality service.
Workflow Chart
Workflow charts help small businesses visualize and improve their processes. Systems and teams use workflow charts to map out tasks, identify bottlenecks, and ensure smooth operations. An effective workflow chart includes several key components:
Involve the right stakeholders.
Keep labels simple and concise.
Use standardized symbols.
Validate with the team.
Iterate and improve regularly.
Highlight key points and decision nodes.
Use color coding for clarity.
Focus on scalability.
Use templates for efficiency.
Workflow charts use basic symbols and shapes to show how tasks move from start to finish. Teams at systems and teams review these charts to find areas for improvement and to train new employees. Regular updates keep processes efficient and support business growth.
Note: Workflow charts help teams visualize steps, spot inefficiencies, and make changes that drive better results.
Financial Spreadsheet
A financial spreadsheet stands as a vital tool for small business owners who want to manage money with accuracy and confidence. This document organizes financial data, tracks spending, and helps leaders make informed decisions. Many owners rely on spreadsheets to monitor income, expenses, and budgets throughout the year.
A well-designed financial spreadsheet includes several key features. The general ledger records monthly income and expenses. Owners categorize these entries by labor, materials, and other costs. This section provides a clear snapshot of where money comes from and where it goes.
Departmental budgets form another important part of the spreadsheet. Each department compares forecasted expenses and revenue with actual results. This process highlights strengths and weaknesses. Leaders use this information to adjust spending and set realistic goals.
Annual business budget templates give a detailed overview of financial activity for the entire year. These templates show trends in revenue and expenses. Owners can spot patterns and plan for seasonal changes. A projections spreadsheet helps set future goals. Departments use these sheets to align their plans and stay on track.
Specific project budget templates allow teams to track income and expenses for individual projects. This feature proves useful for businesses that handle multiple jobs at once. Owners see which projects bring in the most profit and which ones need improvement.
Tip: Regularly updating the financial spreadsheet ensures accuracy and helps prevent costly mistakes.
The table below summarizes the main components of a small business financial spreadsheet:
Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
General Ledger | Tracks monthly income and expenses |
Departmental Budget | Compares forecasted and actual results |
Annual Budget Template | Provides yearly financial overview |
Projections Spreadsheet | Sets future goals and aligns departments |
Project Budget Template | Monitors income and expenses for specific projects |
Many owners use spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets. These programs offer built-in formulas and templates. Users can customize sheets to fit their business needs. Some businesses add charts and graphs to visualize trends and share results with their teams.
A sample spreadsheet might include columns for date, description, category, amount, and notes. Owners enter each transaction and review totals at the end of each month. This habit supports better budgeting and financial planning.
Date | Description | Category | Amount | Notes
---------------------------------------------------------------
2024-06-01 | Office Supplies | Materials | $150.00 | June restock
2024-06-03 | Payroll | Labor | $2,500.00| Weekly wages
2024-06-05 | Website Hosting | Services | $75.00 | Monthly fee
Financial spreadsheets help small businesses stay organized, reduce errors, and prepare for growth. Owners who use these tools gain a clearer understanding of their finances and make smarter decisions for the future.
Essential Tools & Software

Project Management Apps
Small businesses rely on project management apps to organize tasks, monitor progress, and improve teamwork. These tools help teams stay focused and complete projects on time. Popular apps offer features that simplify workflows and boost productivity.
Evernote: Organizes ideas and workflows, providing team storage and easy access to project materials.
Basecamp: Combines document storage, scheduling, and client collaboration in one platform.
Trello: Uses a visual card system for tracking project progress and integrates with other tools.
Slack: Enhances team collaboration with integrations for marketing tools and performance metrics.
Flow: Features Kanban boards for tracking projects and team tasks, ideal for marketing teams.
Asana: Offers multiple visualization options for workflow management, helping teams monitor project statuses.
These project management apps stand out for their ease of use and integration capabilities. They streamline project management processes, improve internal communication, and increase productivity. Teams can assign tasks, set deadlines, and share updates in real time.
Tip: Choosing the right project management app helps small businesses save time and avoid confusion during busy periods.
Communication Platforms
Effective communication platforms keep small business teams connected and organized. These platforms support real-time messaging, video calls, and file sharing, making collaboration easier.
Description | |
|---|---|
Real-Time Messaging | Intuitive chat and organized channels improve communication flow and prevent chaos. |
Video Conferencing | Essential for remote teams, with breakout rooms and screen sharing. |
File Sharing and Storage | Integration with cloud services and version control prevent outdated documents. |
Advanced Search Functionality | Robust search tools help teams find important information quickly. |
Security and Compliance Controls | End-to-end encryption and compliance with regulations protect sensitive data. |
Mobile Accessibility | User-friendly mobile apps keep teams connected while on the move. |
Scalability | Platforms grow with the business, handling more communication as teams expand. |
Analytics and Reporting | Built-in analytics provide insights into team activity and communication effectiveness. |
Communication platforms such as Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Zoom offer these features. They help teams share information, hold meetings, and store files securely. Strong communication tools support teamwork and reduce misunderstandings.
Note: Reliable communication platforms help small businesses respond quickly to clients and adapt to changing needs.
Accounting Software
Accounting software improves financial accuracy and simplifies bookkeeping for small businesses. These tools centralize financial transactions, automate repetitive tasks, and provide clear insights into cash flow.
Centralizes all financial transactions in one system.
Reduces manual errors.
Provides clear insights into cash flow and operational costs.
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Automation | Automates tasks like data entry and invoicing, reducing the likelihood of errors. |
Centralization | Stores financial data in one place, making access and decision-making easier. |
Real-time Reporting | Generates financial statements and reports instantly, supporting data-driven decisions. |
Accounting software such as QuickBooks, Xero, and FreshBooks automates essential bookkeeping tasks and eliminates manual calculations. These programs help owners track income, expenses, and budgets with accuracy. Real-time reporting tools allow leaders to identify trends and make informed decisions.
Tip: Using accounting software helps small businesses maintain accurate records and prepare for growth.
ERP Systems
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems help small businesses manage many processes in one place. These systems combine functions like inventory, sales, finance, and human resources. By using an ERP, a business can reduce manual work and improve accuracy. Teams can see real-time data and make better decisions.
ERP systems offer several benefits. They help owners track inventory, manage orders, and monitor cash flow. Employees can access the same information, which reduces confusion. Many ERPs also automate tasks such as invoicing and payroll. This saves time and lowers the risk of errors.
Choosing the right ERP system is important for long-term growth. Not every ERP fits every business. Owners should look for a system that matches their needs and supports their goals. The following list shows key criteria for selecting an ERP system:
Alignment with Business Needs: The ERP should match the company’s industry and support its main processes.
Functional Requirements: Owners should list the features they need in each department. This helps avoid paying for unnecessary tools.
Scalability and Flexibility: The system should grow with the business and adapt to changes.
Industry-Specific Capabilities: Some ERPs include features for certain industries, such as retail or manufacturing. These can help meet regulations and best practices.
Integration with Existing Systems: The ERP should work well with current software, like accounting or CRM tools.
User Support: All employees should receive training and support to use the system effectively.
Budget and Resources: Owners must consider the total cost, including setup, training, and ongoing fees.
Technology and Future Scalability: The ERP should use modern technology and keep up with future business needs.
The table below compares popular ERP systems for small businesses:
ERP System | Best For | Key Features | Scalability | Integration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
NetSuite | Growing businesses | Financials, CRM, inventory | High | Strong |
SAP Business One | Manufacturing, retail | Accounting, sales, purchasing | Medium | Good |
Odoo | Customization | Modular apps, open source | High | Flexible |
Zoho ERP | Service businesses | Project management, invoicing | Medium | Good |
Note: Owners should involve team members from different departments when choosing an ERP. This ensures the system meets everyone’s needs and supports daily operations.
Selecting the right ERP system helps small businesses organize their processes, save time, and prepare for future growth. A well-chosen ERP becomes the backbone of business operations, supporting efficiency and success.
Consistency & Review
Regular System Checks
Regular system checks help businesses maintain efficiency and prevent problems before they grow. Owners and managers set a schedule for reviewing systems and processes. They check for software updates, security patches, and workflow issues. The frequency of these checks depends on the size and complexity of the business. Many experts recommend the following approach:
Monthly Checks: Review all systems at least once a month. Update software and apply security patches.
Weekly Checks: Examine key processes every week. Catch small issues before they become larger problems.
Daily Checks: Monitor critical systems each day. Address urgent concerns immediately.
A consistent review schedule keeps operations running smoothly. Teams spot inefficiencies early and make quick adjustments. This habit supports long-term growth and stability.
Team Involvement
Team involvement strengthens system reviews and updates. Employees offer valuable insights because they use these systems every day. Owners encourage participation through several methods:
360-degree feedback gathers input from many sources for a complete view.
Regular retrospectives allow teams to discuss what worked and what needs improvement.
Peer recognition programs highlight positive contributions and motivate staff.
Continuous feedback channels give employees a way to share ideas at any time.
Weekly or biweekly one-on-one check-ins help managers and staff solve problems quickly.
Quarterly or biannual performance conversations support long-term growth.
Forward-looking coaching connects feedback to career development.
Goals align employee growth with business objectives.
Involving the team creates a culture of improvement. Employees feel valued and take ownership of their work. This approach leads to better systems and higher morale.
Adapting for Growth
Businesses must adapt their systems as they expand. Growth brings new challenges and requirements. Owners prepare by identifying what needs to change and gathering feedback from the team. They research software that can scale with the business and document current processes to find inefficiencies. Setting clear milestones helps track progress and ensures a smooth transition.
Scalable systems, such as cloud-based solutions, handle increased demands efficiently. Regular evaluations identify areas for improvement and keep systems aligned with business goals. Integrating new technology, like artificial intelligence for customer support, boosts efficiency and responsiveness. As the workforce grows, owners assess scheduling methods and introduce new tools in phases. Strong onboarding procedures help new and existing employees adjust to changes.
Small Business Systems thrive when owners review, involve the team, and adapt to growth. These steps build a foundation for lasting success.
Overcoming Challenges
Change Resistance
Small business owners often face resistance when introducing new systems. Employees may feel uncertain or worry about failing. Emotional reactions can slow progress. Sometimes, staff do not understand the reasons for change. Inadequate training also creates barriers.
Fear of failure
Emotional responses
Inadequate training
Change resistance generally boils down to lack of understanding, which causes uncertainty and even fear.
Leaders can overcome resistance by explaining the benefits of new systems. They should provide clear instructions and offer training sessions. When employees see how systems make their work easier, they become more willing to adapt. Regular feedback and open communication help build trust.
Time Management
Implementing new systems requires careful time management. Owners must balance daily operations with system changes. Effective strategies help teams stay focused and avoid feeling overwhelmed.
Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
Prioritize using the Eisenhower Matrix | Sort tasks by urgency and importance to focus on what matters most. |
Apply the 80/20 rule | Focus on the 20% of tasks that yield 80% of results to maximize efficiency. |
Time block like a boss | Allocate specific time slots for different tasks to maintain focus and reduce chaos. |
Delegate and automate | Offload tasks to others or automate them to free up time for more critical work. |
Limit distractions | Identify and minimize distractions to maintain focus and productivity. |
Say no to multitasking | Concentrate on one task at a time to enhance productivity and reduce errors. |
Get organized—physically and digitally | Maintain an organized workspace to improve efficiency and reduce time lost in searching for items. |
Owners who use these strategies can manage their time better. They focus on important tasks and avoid distractions. Delegation and automation free up hours for planning and growth. Organized workspaces also help teams find what they need quickly.
Budget Constraints
Budget limitations challenge many small businesses. Owners may worry about the cost of new tools or systems. However, affordable solutions exist that support systemization without straining finances.
Asana: A project management tool that helps organize tasks and track progress, with a free plan for up to 15 team members.
Calendly: Simplifies scheduling by allowing others to book time based on your availability, integrating with Google and Outlook calendars.
Slack: A communication platform that organizes team chats and file sharing, with a free tier that includes integrations.
Free and low-cost software options allow small businesses to start organizing systems right away. Owners can choose tools that match their needs and upgrade as the business grows. Careful planning and research help maximize value while keeping expenses low.
Tip: Start with free versions of essential tools. Upgrade only when the business needs more features or capacity.
Small businesses can overcome challenges by addressing resistance, managing time wisely, and choosing budget-friendly solutions. These steps make system implementation smoother and support long-term growth.
Organizing Small Business Systems brings growth, efficiency, and less stress to every team. Many owners begin by identifying the seven main systems in their business. They focus on leadership, marketing, finance, and management. Teams address customer fulfillment, lead conversion, and lead generation. Using a clear framework helps set goals and assign responsibility. Small, steady changes build momentum and lead to big improvements. Readers can reach out to learn how systems and teams support similar results.
FAQ
What is a small business system?
A small business system is a set of organized processes or tools that help a company run smoothly. These systems include marketing, finance, operations, and communication. Owners use systems to save time and reduce mistakes.
How does automation benefit small businesses?
Automation handles repetitive tasks like sending emails or tracking inventory. Teams gain more time for important work. Automation also lowers the risk of errors and improves consistency.
Which area should a business systemize first?
Owners often start with finance or client communication. These areas impact cash flow and customer satisfaction. Systemizing them helps businesses see quick improvements.
What tools help organize business systems?
Project management apps, accounting software, and communication platforms help teams stay organized. Many owners use tools like Trello, QuickBooks, and Slack to manage tasks and share information.
How often should systems be reviewed?
Teams should review systems monthly. Regular checks help spot problems early and keep processes efficient. Owners update tools and workflows as the business grows.
Can small businesses afford systemization?
Many free or low-cost tools support systemization. Owners choose software that fits their budget. Starting small and upgrading later helps control costs.
What is process mapping?
Process mapping shows each step in a workflow. Owners use flowcharts or diagrams to find problems and improve efficiency. Teams follow the map to complete tasks correctly.
How does delegation support growth?
Delegation assigns tasks to team members or contractors. Owners focus on strategy while others handle routine work. This approach increases productivity and supports business expansion.



